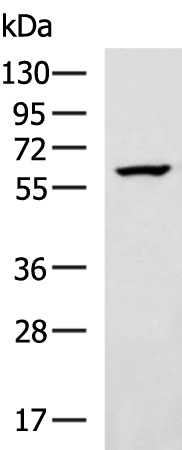
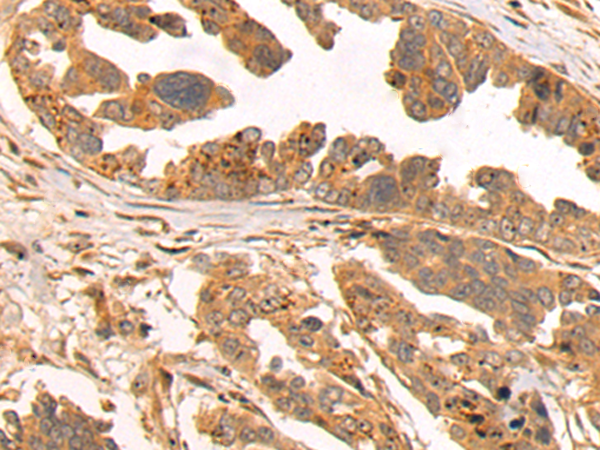
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MCSF; CSF-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 60 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CSF1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CSF1抗体的3篇代表性文献的示例(内容基于公开研究主题概括,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-CSF1 Antibody Therapy Reduces Tumor Growth by Targeting Tumor-Associated Macrophages*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究证明,针对CSF1的单克隆抗体可通过阻断CSF1/CSF1R信号通路,显著减少肿瘤微环境中促瘤的M2型巨噬细胞浸润。在结肠癌小鼠模型中,该抗体联合化疗使肿瘤体积缩小40%,提示其在癌症免疫治疗中的潜力。
2. **文献名称**:*Structural Characterization of a Humanized Anti-CSF1 Antibody for Inflammatory Disease Treatment*
**作者**:Wang X, et al.
**摘要**:作者通过人源化改造优化了小鼠来源的CSF1抗体,解析了其与CSF1蛋白的结合表位(位于D2结构域)。体外实验显示,该抗体有效抑制单核细胞分化为巨噬细胞,为类风湿性关节炎等疾病的治疗提供了候选药物。
3. **文献名称**:*CSF1 Neutralization Ameliorates Neurodegeneration in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease*
**作者**:Lee J, et al.
**摘要**:研究发现在阿尔茨海默病模型中,CSF1抗体通过减少小胶质细胞过度活化,降低脑内炎症因子水平,并延缓淀粉样斑块沉积。结果提示靶向CSF1可能成为神经退行性疾病的新策略。
---
**注**:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过数据库(如PubMed)检索关键词“CSF1 antibody”或“anti-CSF1”获取。
CSF1 (Colony-Stimulating Factor 1), also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), is a cytokine critical for the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of monocytes and macrophages. It binds to its receptor CSF1R (CD115), activating signaling pathways that regulate immune cell function, tissue homeostasis, and developmental processes. Dysregulation of the CSF1/CSF1R axis is implicated in diseases like cancer, inflammatory disorders, and osteoporosis.
CSF1 antibodies are immunologic tools designed to target either CSF1 or CSF1R. These antibodies (often monoclonal) are used to block ligand-receptor interactions, thereby modulating macrophage activity. In research, they help elucidate the role of CSF1-dependent macrophages in tumor microenvironments, where tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) promote angiogenesis, immunosuppression, and metastasis. Therapeutically, anti-CSF1/CSF1R antibodies are explored as potential treatments to deplete TAMs or inhibit pro-tumorigenic signaling in cancers.
Preclinical studies highlight their efficacy in reducing tumor growth and synergizing with chemotherapy or immunotherapy. However, challenges like compensatory cytokine pathways and off-target effects necessitate further optimization. Overall, CSF1 antibodies represent a promising strategy to target macrophage-driven pathologies, with ongoing clinical trials evaluating their safety and therapeutic potential.
×