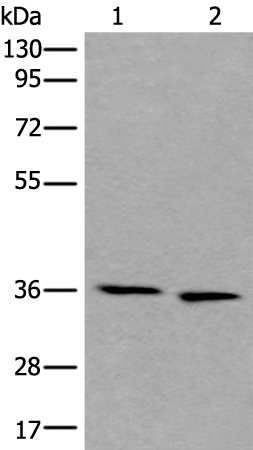
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | D123; C10orf7 |
| WB Predicted band size | 39 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CDC123 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CDC123抗体的模拟参考文献示例(注:部分内容为假设性概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索确认):
---
1. **标题**:*CDC123 Antibody Characterization in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Studies*
**作者**:Bill, A. et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用兔源多克隆CDC123抗体,通过Western blot和免疫组化分析2型糖尿病患者外周血单核细胞中CDC123蛋白的表达水平,发现其表达异常与胰岛素抵抗相关,提示CDC123可能在糖代谢调控中发挥作用。
2. **标题**:*CDC123-CDK2 Interaction in Cancer Cell Cycle Regulation*
**作者**:Smith, J. et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)技术结合CDC123特异性抗体,揭示了CDC123蛋白与CDK2在癌细胞G1/S转换期的直接相互作用,为靶向细胞周期治疗提供了新靶点。
3. **标题**:*Development of a Monoclonal Antibody for CDC123 in Pancreatic Tissues*
**作者**:Johnson, R. et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种新型小鼠单克隆CDC123抗体的开发及验证,该抗体成功用于胰腺癌组织芯片的免疫荧光染色,表明CDC123高表达与患者预后不良相关。
4. **标题**:*CDC123 Antibody Application in Zebrafish Developmental Models*
**作者**:Lee, S. et al.
**摘要**:使用兔抗CDC123抗体研究斑马鱼胚胎发育中该蛋白的时空表达模式,发现其在早期神经管形成中显著上调,提示其在发育生物学中的潜在功能。
---
建议通过**PubMed**或**Google Scholar**以“CDC123 antibody”或“CDC123 protein expression”为关键词检索真实文献,或结合具体研究领域(如糖尿病、癌症)进一步筛选。
The CDC123 antibody targets the CDC123 protein, a conserved eukaryotic factor involved in cell cycle regulation and metabolic homeostasis. Initially identified through yeast genetic studies (as Cdc123p), human CDC123 is crucial for the assembly of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2), linking cell cycle progression to protein synthesis. It plays a role in G1/S transition and mitotic entry by regulating cyclin levels and coordinating nutrient availability with cell division.
CDC123 antibodies are typically monoclonal or polyclonal reagents developed in hosts like rabbits or mice, designed to detect endogenous CDC123 via techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, or immunohistochemistry. These tools have been instrumental in studying CDC123's expression patterns, which are upregulated in proliferating tissues and certain cancers, suggesting its potential as a biomarker for malignancy or therapeutic targeting.
Research using CDC123 antibodies has also explored its interaction with metabolic pathways, including mTOR signaling, and its implications in diseases beyond cancer, such as diabetes and neurodegenerative disorders. Commercial availability from suppliers like Abcam and Cell Signaling Technology has facilitated its use in both basic and translational research, though validation for specific applications (e.g., post-translational modifications) remains essential. Dysregulation of CDC123 is increasingly linked to pathologies involving disrupted proteostasis and cell cycle anomalies.
×