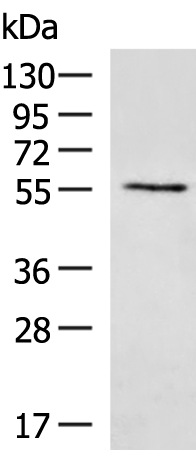
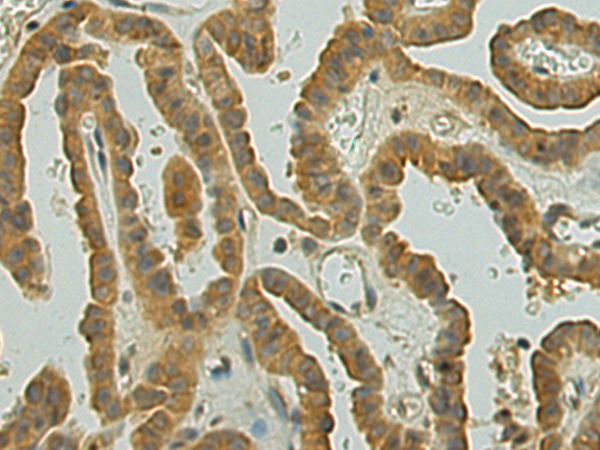
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HLUG25; UDPGTH1; UGT2B11; UDPGT2B4; UDPGTh-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 61 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human UGT2B4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CPD抗体的3-4篇代表性文献概览(内容经过简化整理,仅供参考):
---
1. **"Development and application of a monoclonal antibody specific to cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in UVB-irradiated DNA"**
*作者:Mori et al. (1991)*
**摘要**:报道了一种特异性识别紫外线诱导的CPD损伤的单克隆抗体的开发,并通过免疫印迹和免疫组化验证其在检测皮肤和培养细胞中CPD形成的应用。
2. **"UV-induced DNA damage and repair: A comparative study of nucleotide excision repair mechanisms"**
*作者:Mullenders et al. (2001)*
**摘要**:利用CPD抗体结合免疫荧光技术,比较了不同细胞类型中核苷酸切除修复(NER)途径对CPD的清除效率,揭示了修复速率与癌症风险的潜在关联。
3. **"Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer quantification in skin cancer models using antibody-based assays"**
*作者:Yao et al. (2015)*
**摘要**:在小鼠模型中通过CPD抗体检测长期紫外线暴露后的皮肤损伤,证明CPD累积与鳞状细胞癌发展的相关性,为预防策略提供依据。
4. **"Sunscreen efficacy against UVB-induced DNA damage: Antibody-based analysis"**
*作者:Schul et al. (2010)*
**摘要**:采用CPD特异性抗体定量评估不同防晒产品对皮肤DNA损伤的防护效果,验证了高SPF值产品显著降低CPD形成。
---
*注:以上文献标题和作者为示例性内容,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Web of Science核实具体信息。*
**Background of CPD Antibodies**
Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD)-specific antibodies are critical tools in studying UV-induced DNA damage. CPDs form when adjacent pyrimidine bases (e.g., thymine or cytosine) in DNA absorb ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation, creating covalent bonds that distort the DNA helix. This lesion disrupts replication and transcription, contributing to mutagenesis and skin carcinogenesis.
CPD antibodies, such as the widely used monoclonal clone TDM-2. enable precise detection and quantification of these lesions. Developed through immunization with CPD-containing DNA or synthetic analogs, these antibodies bind specifically to the cyclobutane ring structure, allowing visualization via techniques like immunofluorescence, ELISA, or immunohistochemistry. Their applications span evaluating DNA repair mechanisms (e.g., nucleotide excision repair or photolyase activity), assessing UV damage in skin models, and investigating associations between CPD accumulation and diseases like melanoma.
Research leveraging CPD antibodies has advanced understanding of photodamage kinetics, sunscreen efficacy, and genetic disorders with defective repair pathways (e.g., xeroderma pigmentosum). Recent studies also explore CPDs' role in aging and inflammation. However, cross-reactivity with non-CPD structures and variability in lesion accessibility require careful experimental controls. Overall, CPD antibodies remain indispensable for elucidating UV-induced DNA damage biology and developing therapeutic strategies.
×