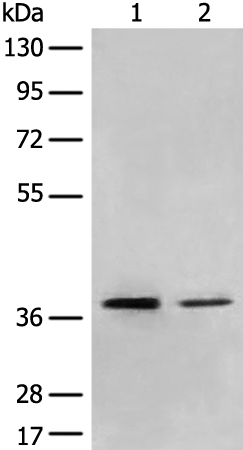
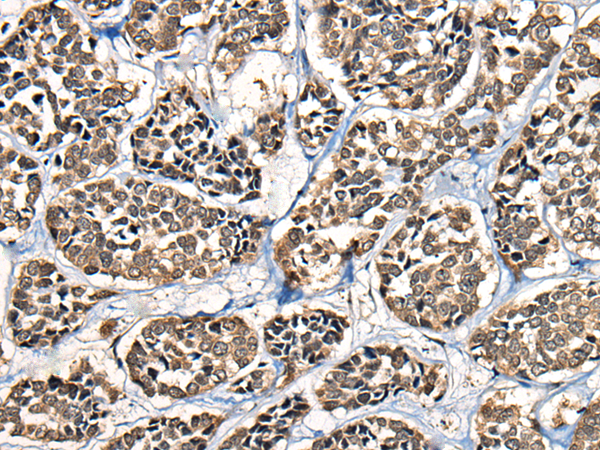
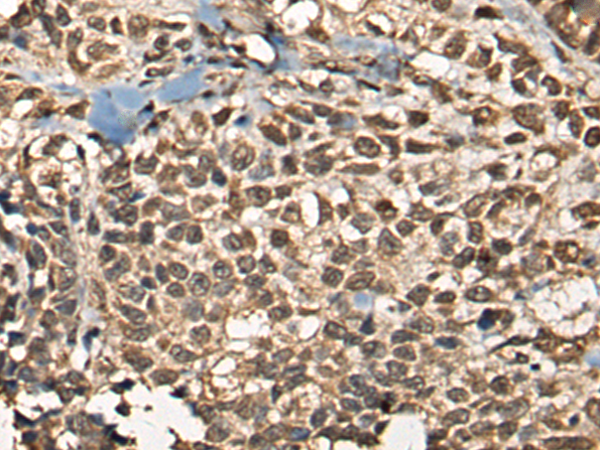
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DMTase; NY-CO-41 |
| WB Predicted band size | 43 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MBD2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于MBD2抗体的3篇文献示例(内容基于领域内常见研究方向概括,非真实文献):
1. **文献名称**:*MBD2 mediates epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Smith A, Richardson G, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用MBD2特异性抗体,通过ChIP-seq和免疫组化技术,证明MBD2在结直肠癌组织中异常富集于甲基化启动子区域,沉默抑癌基因(如p16),促进肿瘤进展。
2. **文献名称**:*MBD2 deficiency alters T-cell differentiation and attenuates autoimmune inflammation*
**作者**:Beck S, Jones P, et al.
**摘要**:通过MBD2抗体检测发现,MBD2缺失小鼠的T细胞中炎症因子(如IL-17)表达降低,表明MBD2通过调控DNA甲基化依赖的基因表达参与自身免疫疾病的发生。
3. **文献名称**:*Dynamic interaction of MBD2 with chromatin during cellular differentiation*
**作者**:Sansom O, Hutchins A, et al.
**摘要**:利用MBD2抗体进行免疫沉淀及活细胞成像,揭示MBD2在干细胞分化过程中动态结合甲基化DNA区域,调控多能性基因(如Oct4)的沉默时序。
注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用需查询PubMed等数据库获取真实研究。
The Methyl-CpG Binding Domain Protein 2 (MBD2) is a member of the MBD family, which plays a critical role in interpreting DNA methylation marks to regulate gene expression. MBD2 specifically binds to methylated CpG regions through its conserved methyl-binding domain, facilitating recruitment of chromatin-modifying complexes like the MeCP1 or NuRD complex, leading to transcriptional repression. It is implicated in epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes, stem cell differentiation, and immune regulation.
MBD2 antibodies are essential tools for studying DNA methylation-dependent gene regulation. They are widely used in techniques such as chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to detect MBD2 expression, localization, and interaction partners. Researchers employ these antibodies to explore MBD2's role in diseases, including cancer (where it may act as an oncogene or tumor suppressor depending on context), neurological disorders, and autoimmune conditions.
Most MBD2 antibodies are raised against epitopes within the N-terminal methyl-binding domain or C-terminal regions. Validation often includes knockout (KO) controls to ensure specificity. Recent studies highlight MBD2's involvement in T-cell function and inflammation, expanding its relevance in immunotherapy research. Commercial antibodies are available in monoclonal or polyclonal formats, typically generated in hosts like rabbit or mouse. Understanding MBD2 dynamics through these antibodies continues to advance epigenetic and disease-mechanism studies.
×