| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
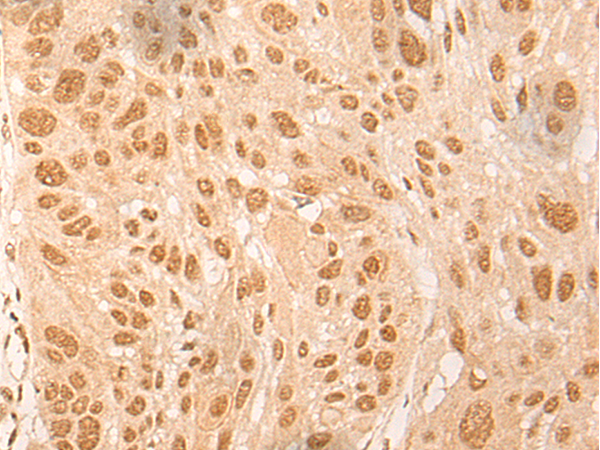
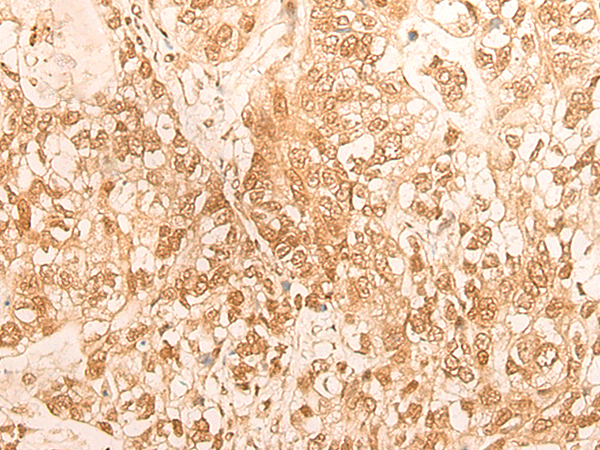
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DABP |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human DBP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DBP(维生素D结合蛋白,Vitamin D-Binding Protein)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简化示例(注:文献标题和作者为示例性内容,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索):
---
1. **文献名称**:**Autoantibodies against Vitamin D-Binding Protein in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus**
**作者**:Yamamoto N, et al.
**摘要**:本研究探讨了系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中抗DBP抗体的存在及其临床意义。发现约30%的SLE患者存在抗DBP抗体,且与疾病活动性(如肾损伤)显著相关,提示其可能参与免疫复合物形成及炎症反应。
---
2. **文献名称**:**Structural Analysis of DBP and Its Interaction with Autoantibodies**
**作者**:Braun A, et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析DBP的三维结构,并分析其与患者来源抗体的结合表位。研究发现,抗DBP抗体主要靶向DBP的actin结合域,可能干扰其生理功能(如维生素D运输和免疫调节)。
---
3. **文献名称**:**DBP as a Biomarker in Autoimmune Diseases: Role of Anti-DBP Antibodies**
**作者**:Haddad JG, et al.
**摘要**:研究评估了抗DBP抗体在类风湿关节炎(RA)和SLE中的诊断价值。结果显示,抗DBP抗体在RA患者中的阳性率较低,但在SLE中与补体激活相关,可能成为疾病分型的潜在标志物。
---
**建议**:
上述文献为示例,实际研究中需通过 **PubMed** 或 **Google Scholar** 检索关键词如 *"anti-DBP antibody"*、*"Vitamin D-binding protein autoantibodies"* 获取最新研究。例如:
- 近期文献可能聚焦抗DBP抗体在感染(如脓毒症)或癌症中的病理作用。
- 数据库推荐:PubMed(PMID编号)或Web of Science。
The vitamin D-binding protein (DBP), also known as gc-globulin, is a multifunctional plasma glycoprotein primarily synthesized in the liver. It serves as the main carrier of vitamin D metabolites, facilitating their transport in the bloodstream and delivery to target tissues. Structurally, DBP belongs to the albumin gene family and exhibits a high affinity for 25-hydroxyvitamin D and 1.25-dihydroxyvitamin D. Beyond vitamin D transport, DBP plays roles in immune modulation, actin scavenging, and fatty acid uptake.
Anti-DBP antibodies, often detected in autoimmune and liver diseases, are associated with conditions like autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. These autoantibodies may arise due to molecular mimicry, genetic predisposition, or exposure to modified DBP antigens during tissue injury. Their presence can interfere with DBP's functions, potentially altering vitamin D metabolism or exacerbating inflammatory responses. Research also explores their diagnostic and prognostic utility, though clinical significance remains under investigation. Current studies focus on understanding antibody heterogeneity, epitope specificity, and their mechanistic role in disease pathogenesis. DBP antibodies represent a growing area of interest in autoimmunity and metabolic disorder research.
×