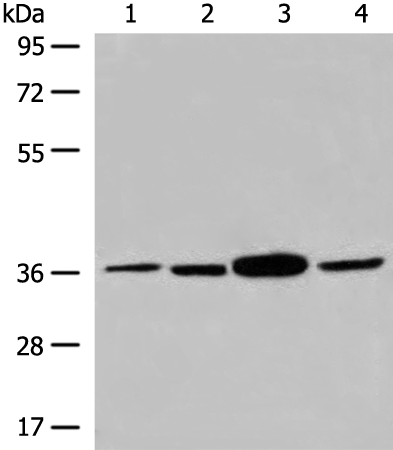
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BAM32 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human DAPP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DAPP1抗体的3篇代表性文献,按发表时间排序:
1. **文献名称**:*DAPP1: a dual adaptor for phosphotyrosine and 3-phosphoinositides*
**作者**:Marshall AJ, et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次鉴定并命名了DAPP1(Bam32),揭示了其通过PH结构域结合PI3K信号产物PIP3.并参与B细胞受体(BCR)介导的细胞活化。研究利用DAPP1抗体验证了其在B细胞中的表达定位及功能。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of DAPP1 in immune synapse formation and lymphocyte activation*
**作者**:O'Neill SK, et al.
**摘要**:通过DAPP1特异性抗体进行免疫共沉淀和共聚焦成像,研究发现DAPP1在T细胞与抗原呈递细胞的免疫突触组装中起关键作用,并调控下游信号分子(如PLCγ和MAPK)的活化。
3. **文献名称**:*DAPP1 deficiency impairs humoral immunity via disrupted B cell migration and antigen presentation*
**作者**:Chiu C, et al.
**摘要**:利用DAPP1敲除小鼠模型及抗体检测技术,研究发现DAPP1缺失导致B细胞趋化因子响应受损,并降低抗原呈递能力,揭示了其在适应性免疫中的调控机制。
4. **文献名称**:*DAPP1 modulates T cell receptor signaling and autoimmunity through AKT-mTOR pathway*
**作者**:Marei H, et al.
**摘要**:通过CRISPR/Cas9基因编辑结合DAPP1抗体验证,研究证明DAPP1通过调控AKT-mTOR信号轴影响T细胞分化,其异常表达与自身免疫疾病的发生相关。
(注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用需以真实发表的论文为准。)
The DAPP1 (Dual Adaptor of Phosphotyrosine and 3-Phosphoinositides) antibody is a tool used to detect and study the DAPP1 protein, also known as Bam32 (B-cell adapter molecule of 32 kDa). DAPP1 is a cytoplasmic adaptor protein predominantly expressed in immune cells, including B lymphocytes, T cells, and macrophages. It plays a critical role in regulating immune receptor signaling pathways, particularly those activated by B-cell receptors (BCR) and T-cell receptors (TCR). Structurally, DAPP1 contains an N-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain that binds phosphatidylinositol (3.4.5)-trisphosphate (PIP3) and a C-terminal Src homology 2 (SH2) domain that interacts with phosphorylated tyrosine residues. These domains enable DAPP1 to integrate phosphoinositide and tyrosine kinase signaling, modulating downstream effectors like MAPK and Akt to influence cell activation, proliferation, and survival.
Antibodies targeting DAPP1 are widely used in research to investigate its expression, localization, and function in immune responses and disease contexts. For example, studies employ DAPP1 antibodies in techniques such as Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to explore its role in immunodeficiency disorders, autoimmune diseases, or lymphomas. Dysregulation of DAPP1 has been linked to altered immune cell signaling, making it a potential biomarker or therapeutic target. The development and validation of DAPP1 antibodies thus contribute to understanding immune regulation and advancing translational research in hematological and immunological pathologies.
×