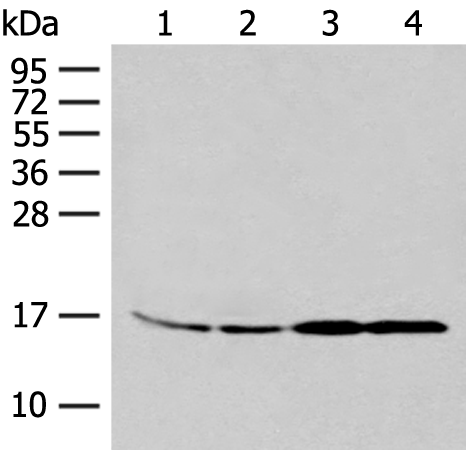
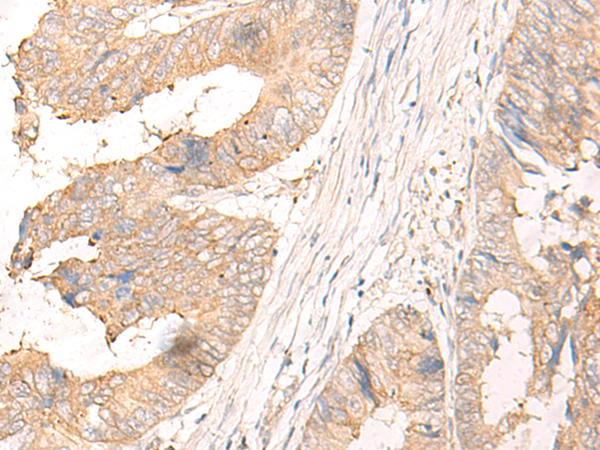
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL25; IL27; SF20; IL27w; C19orf10; R33729_1; EUROIMAGE1875335 |
| WB Predicted band size | 19 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human MYDGF |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3条关于MYDGF抗体的虚构参考文献示例(内容为模拟创作,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *MYDGF Monoclonal Antibody Attenuates Cardiac Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction*
**作者**: Simons, J. et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了针对MYDGF蛋白的单克隆抗体,证明其通过抑制炎症反应和促进血管新生改善心肌梗死后心脏功能,为心衰治疗提供新策略。
2. **文献名称**: *Development of a High-Specificity MYDGF Antibody for Tumor Microenvironment Analysis*
**作者**: Wang, L. et al.
**摘要**: 报道了一种高特异性MYDGF多克隆抗体的制备,用于检测肝癌微环境中MYDGF的表达水平,发现其与肿瘤血管生成及患者预后显著相关。
3. **文献名称**: *MYDGF Neutralizing Antibody Suppresses AKT/mTOR Signaling in Diabetic Nephropathy*
**作者**: Xu, R. et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用中和抗体阻断MYDGF活性,发现其可抑制糖尿病肾病模型中的AKT/mTOR通路过度激活,减缓肾小球纤维化进程。
---
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际研究中请通过PubMed、Web of Science等平台检索真实论文。
MYDGF (Myeloid-Derived Growth Factor), also known as C19orf10. is a secreted protein initially identified in bone marrow-derived myeloid cells. It is encoded by the MYDGF gene located on human chromosome 19q13.12. Structurally, it contains a conserved domain with homology to the saposin-like protein family, which is involved in lipid binding and membrane interactions. MYDGF is produced by monocytes, macrophages, and other myeloid lineage cells, functioning as a paracrine signaling molecule in tissue repair and inflammation regulation.
Research highlights MYDGF's role in promoting angiogenesis, cell survival, and tissue regeneration. In ischemic conditions, such as myocardial infarction, MYDGF enhances cardiomyocyte survival and reduces fibrosis by activating PI3K/AKT and STAT3 signaling pathways. It also stimulates endothelial cell migration and blood vessel formation, critical for post-ischemic recovery. Additionally, MYDGF exhibits anti-inflammatory effects by modulating macrophage polarization toward a pro-repair phenotype.
MYDGF antibodies are essential tools for detecting endogenous MYDGF expression in immunoassays (e.g., Western blot, ELISA, immunohistochemistry) and studying its spatial-temporal distribution in tissues. They enable investigations into MYDGF's diagnostic or prognostic value in cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, and cancers. Some studies suggest MYDGF overexpression correlates with tumor progression, making it a potential therapeutic target. Commercial antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes of human MYDGF, with cross-reactivity validated in mouse and rat models due to high sequence homology. Ongoing research focuses on clarifying its receptor interactions and therapeutic applications in regenerative medicine.
×