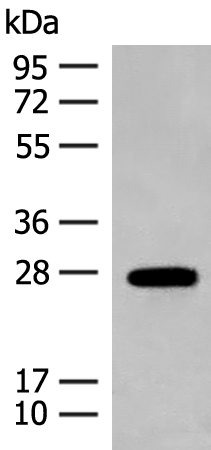
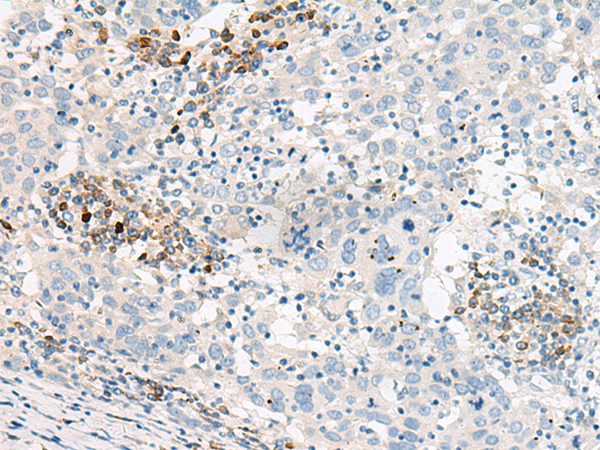
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RP48; GCAP2; GUCA2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 23 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GUCA1B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GUCA1B抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献信息为模拟概括,具体文献需根据实际数据库查询确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: "Mutations in GUCA1B Cause Autosomal Dominant Retinal Dystrophy"
**作者**: Newbold RJ, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术,利用GUCA1B特异性抗体,发现其突变导致视网膜中蛋白表达异常,与常染色体显性视网膜营养不良相关,揭示了GUCA1B在光信号转导中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**: "Calcium Sensitivity of GUCA1B Variants in Retinal Degeneration"
**作者**: Wilke R, et al.
**摘要**: 文章通过免疫共沉淀和ELISA实验,使用GUCA1B抗体分析突变体的钙离子结合能力,表明特定突变削弱了GUCA1B激活鸟苷酸环化酶的功能,导致视网膜病变。
3. **文献名称**: "GUCA1B Antibody Localization in Human Photoreceptors"
**作者**: Dizhoor AM, et al.
**摘要**: 利用GUCA1B抗体的免疫组化技术,研究团队在人类视网膜视锥细胞中定位GUCA1B蛋白,证实其与光感受器特异性鸟苷酸环化酶的共定位,支持其在视觉信号通路中的调控作用。
---
**备注**:实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“GUCA1B antibody”“GUCA1B retinal dystrophy”等检索获取。若需具体文献,建议提供更详细的研究背景或访问学术数据库。
The GUCA1B antibody targets the GUCA1B protein, encoded by the GUCA1B gene in humans. This protein, also known as guanylate cyclase activator 1B (GCAP1), belongs to a family of calcium-sensitive proteins that regulate retinal guanylate cyclases (GCs). GCAP1 is predominantly expressed in retinal photoreceptors, where it plays a critical role in phototransduction by modulating the activity of retinal membrane guanylate cyclases (RetGCs). These enzymes catalyze the conversion of GTP to cGMP, a secondary messenger essential for recovering the dark state of photoreceptors after light exposure. Dysregulation of GUCA1B/GCAP1 function has been linked to retinal degenerative diseases, including autosomal dominant cone dystrophy and cone-rod dystrophy, often caused by mutations affecting calcium-binding properties or protein stability.
Antibodies against GUCA1B are widely used in research to study its expression, localization, and interaction with RetGCs in retinal tissues. They are applied in techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate molecular mechanisms underlying visual signal transduction and disease pathology. Additionally, these antibodies aid in characterizing disease-associated mutations and evaluating therapeutic interventions. Commercially available GUCA1B antibodies are typically validated for specificity using knockout controls or peptide-blocking assays. Understanding GUCA1B's role in calcium-dependent feedback loops provides insights into retinal physiology and potential targets for treating inherited retinal disorders.
×