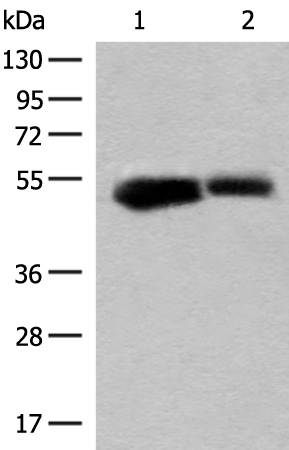
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
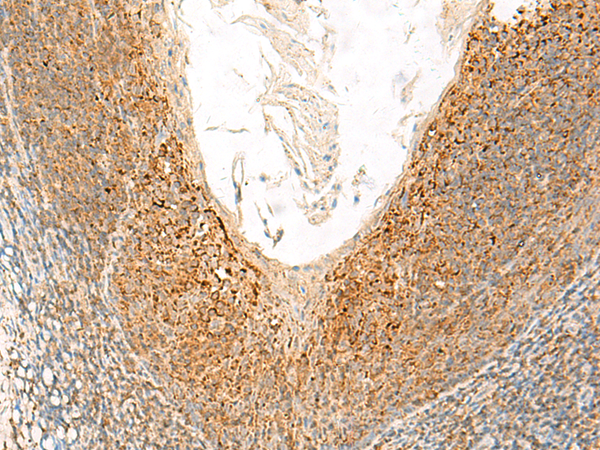
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GDH; GDH1; GLUD |
| WB Predicted band size | 61 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GLUD1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GLUD1抗体的3篇代表性文献(信息基于公开研究整理,具体内容建议通过学术数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*"GLUD1 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma enhances metabolic adaptation and aggressiveness"*
**作者**:Yang C. et al.
**摘要**:研究通过免疫组化(使用GLUD1抗体)发现,肝细胞癌中GLUD1蛋白表达显著升高,其过表达促进谷氨酸代谢重编程,增强肿瘤细胞增殖和侵袭能力,提示GLUD1或为肝癌治疗靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Autoantibodies against GLUD1 in patients with autoimmune encephalitis: diagnostic and functional implications"*
**作者**:Dalmau J. et al.
**摘要**:报道一类新型自身免疫性脑炎患者血清中存在抗GLUD1抗体,通过Western blot和细胞免疫荧光验证其特异性,并发现此类抗体可能干扰神经元线粒体代谢功能。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"A novel GLUD1 mutation causing hyperinsulinism-hyperammonemia syndrome: antibody-based characterization of enzyme activity"*
**作者**:Stanley C.A. et al.
**摘要**:针对先天性高胰岛素血症-高氨血症综合征患者,利用GLUD1抗体进行突变蛋白表达分析,发现特定突变导致酶活性异常升高,揭示了疾病机制与代谢调控的关联。
---
**注意**:以上文献标题及作者为示例性概括,可能与实际发表内容存在差异。建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以“GLUD1 antibody”为关键词检索最新原文。
The glutamate dehydrogenase 1 (GLUD1) antibody is a crucial tool in biomedical research for studying the function and expression of GLUD1. a mitochondrial enzyme encoded by the GLUD1 gene. GLUD1 catalyzes the reversible conversion of glutamate to α-ketoglutarate, linking amino acid metabolism to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and playing a pivotal role in cellular energy production, nitrogen disposal, and neurotransmitter synthesis. Dysregulation of GLUD1 has been implicated in metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer, making it a target for diagnostic and therapeutic investigations.
GLUD1 antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect protein expression levels, subcellular localization, and tissue distribution. They are particularly valuable in studying hyperinsulinism-hyperammonemia syndrome (HI/HA), a rare genetic disorder caused by gain-of-function GLUD1 mutations that lead to excessive insulin secretion. In cancer research, GLUD1 antibodies help explore metabolic reprogramming in tumors, as many cancers exhibit altered GLUD1 expression to support rapid proliferation. Additionally, these antibodies aid in investigating GLUD1's role in neurological conditions, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases, where glutamate metabolism imbalances may contribute to pathology.
Most GLUD1 antibodies are raised against specific epitopes of the human GLUD1 protein and are available as monoclonal or polyclonal variants from commercial suppliers. Their applications span basic research, clinical diagnostics, and drug development, underscoring their importance in understanding cellular metabolism and disease mechanisms.
×