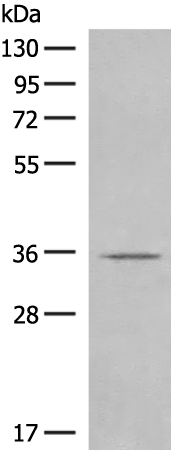
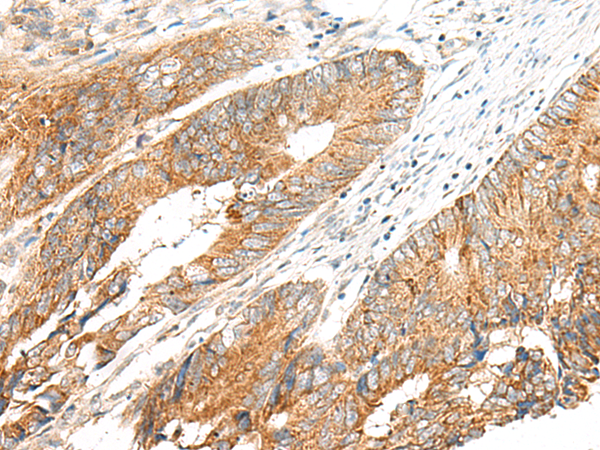
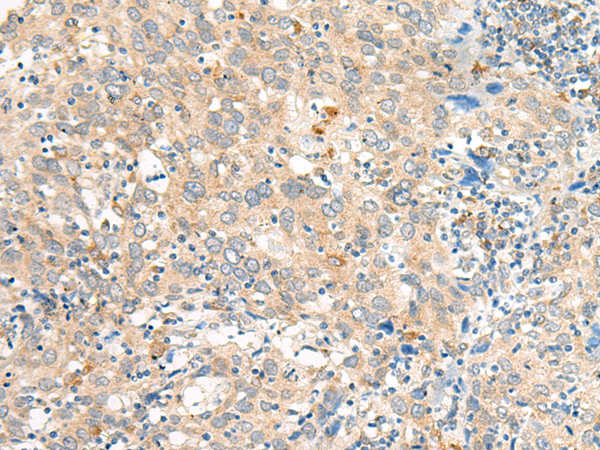
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GPCR2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 37 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GPR119 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于GPR119抗体的代表性文献(基于公开研究,部分信息可能需核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Development of a Novel Monoclonal Antibody Against GPR119 for Immunohistochemical Analysis*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究团队开发了一种高特异性GPR119单克隆抗体,并通过Western blot和免疫组化验证其在人胰腺和肠道组织中的表达,证明其适用于受体定位研究,为糖尿病相关机制研究提供工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*GPR119 Agonist Antibody Enhances Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion in Diabetic Models*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种具有激动剂活性的GPR119抗体,在糖尿病小鼠模型中通过激活受体显著促进葡萄糖依赖性胰岛素分泌,提示其在代谢疾病治疗中的潜在应用价值。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Characterization of GPR119 Receptor Dynamics Using Fluorescent-Labeled Antibodies*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:研究者利用荧光标记的GPR119抗体实时追踪受体在细胞膜上的内吞和循环过程,揭示了GPR119在脂质代谢信号传导中的动态调控机制。
---
**备注**:若需获取具体文献全文,建议通过PubMed或Sci-Hub输入标题/作者查询。部分较新研究可能需访问期刊官网。
GPR119 (G Protein-Coupled Receptor 119) is a class A GPCR predominantly expressed in pancreatic β-cells and intestinal L-cells, where it plays a role in glucose homeostasis and energy metabolism. It is activated by endogenous lipid-derived ligands, such as oleoylethanolamide (OEA) and 2-monoacylglycerol, which stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) release from intestinal cells. This dual action makes GPR119 a therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes and obesity.
GPR119 antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and signaling mechanisms. They are used in immunoassays (e.g., Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry) to quantify receptor levels in tissues or assess its regulation under metabolic conditions. Both polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies have been developed, often targeting extracellular or intracellular epitopes to study receptor trafficking or ligand interactions. Challenges in antibody development include GPR119's low endogenous expression and structural homology with other GPCRs, requiring rigorous validation to ensure specificity.
Research using GPR119 antibodies has clarified its role in nutrient-sensing pathways and informed drug discovery efforts, including the design of GPR119 agonists. However, clinical trials of such agonists have shown mixed results, highlighting the need for deeper mechanistic insights. Reliable antibodies remain essential for unraveling GPR119's physiology and optimizing therapeutic strategies.
×