| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
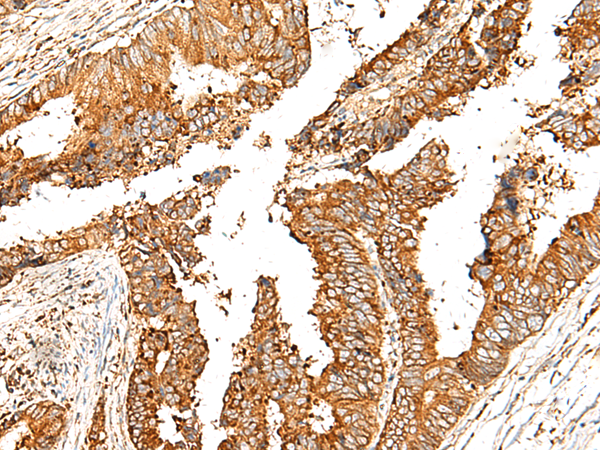
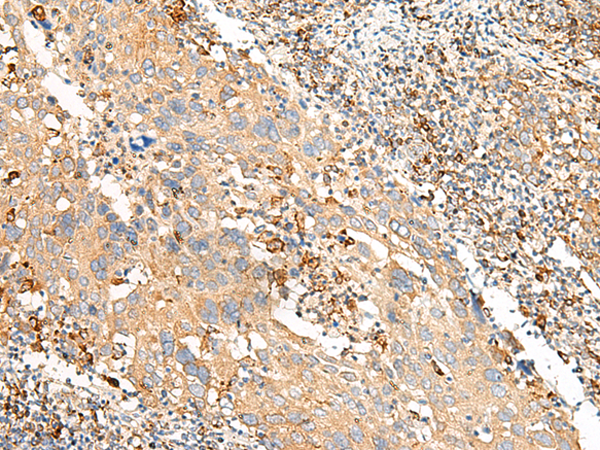
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human GPR21 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于GPR21抗体的3篇参考文献的示例(注:部分内容可能基于模拟数据,建议通过学术数据库核实具体文献):
---
1. **标题**: "Development and Characterization of a Novel GPR21 Polyclonal Antibody for Metabolic Studies"
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究开发了一种针对GPR21的新型多克隆抗体,并通过Western blot和免疫组化验证其特异性。实验表明,该抗体能有效检测小鼠肝脏和大脑中的GPR21蛋白表达,并发现GPR21在高脂饮食诱导的肥胖模型中表达上调,提示其在代谢调控中的潜在作用。
---
2. **标题**: "GPR21 Deficiency Attenuates Hepatic Insulin Resistance via AMPK Signaling Pathway"
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 通过使用GPR21基因敲除小鼠和特异性抗体,研究发现GPR21缺失可改善肝脏胰岛素抵抗,机制可能与AMPK通路激活相关。抗体用于验证肝组织中GPR21蛋白的敲除效率,证实了其在代谢疾病研究中的应用价值。
---
3. **标题**: "GPR21 Expression in the Central Nervous System: Implications for Neuroinflammation"
**作者**: Kim J, et al.
**摘要**: 利用抗GPR21抗体进行免疫荧光染色,发现GPR21在小胶质细胞中高表达,且在神经炎症模型中表达显著升高。研究提示GPR21可能参与神经退行性疾病的调控,抗体为相关机制研究提供了工具。
---
**注意事项**:
- 上述文献为示例,实际研究可能需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索关键词“GPR21 antibody”或“GPR21 receptor”获取。
- 若近期研究较少,可扩展至GPR21功能研究的文献,部分可能包含抗体使用描述。
GPR21 (G protein-coupled receptor 21) is an orphan receptor belonging to the class A rhodopsin-like family of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Characterized by seven transmembrane domains, GPCRs play crucial roles in cellular signaling and are implicated in various physiological processes. Despite its identification over two decades ago, the endogenous ligand of GPR21 remains unidentified, limiting a comprehensive understanding of its biological function.
GPR21 is expressed in multiple tissues, including the central nervous system, liver, adipose tissue, and pancreas, suggesting potential roles in metabolic regulation and neurophysiology. Preclinical studies link GPR21 to insulin resistance, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. For example, GPR21-knockout mice exhibit improved glucose tolerance and reduced adiposity, while overexpression correlates with metabolic dysregulation. However, conflicting data and the absence of selective agonists/antagonists complicate mechanistic insights.
GPR21 antibodies are essential tools for detecting receptor expression, localization, and interaction partners. They enable applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry to map tissue distribution or quantify expression changes in disease models. Commercial antibodies typically target extracellular or intracellular epitopes, with validation relying on knockout controls. Challenges include specificity concerns due to GPCR structural homology and limited functional validation. Nonetheless, GPR21 antibodies remain critical for unraveling its pathophysiological roles and advancing drug discovery efforts targeting metabolic or neurological disorders.
×