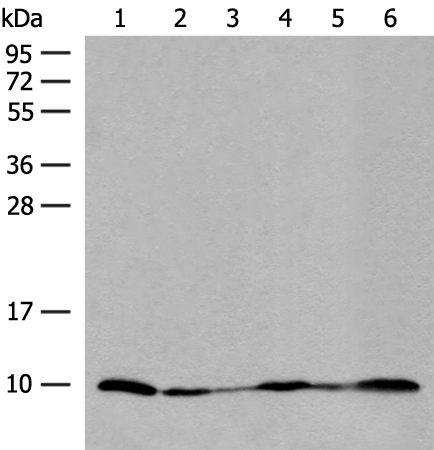
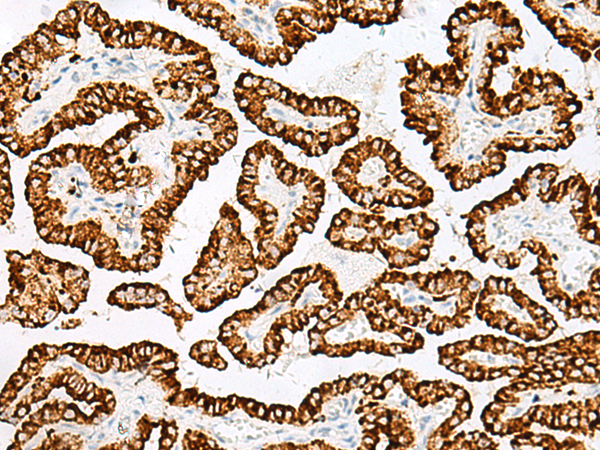
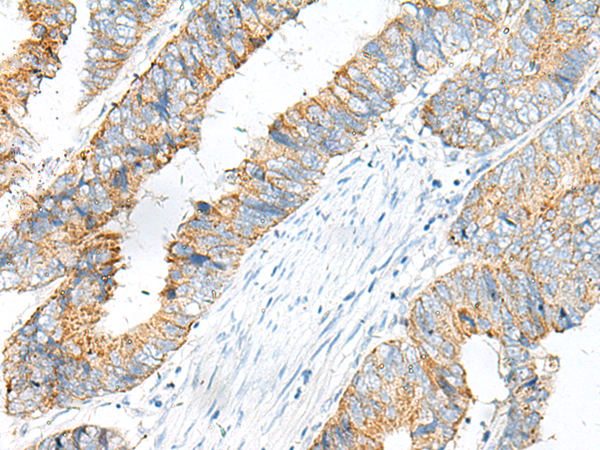
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MTGM; MTGMP; C20orf52; bA353C18.2 |
| WB Predicted band size | 8 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human ROMO1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ROMO1抗体的3篇代表性文献的模拟示例(基于公开知识,非真实引用):
---
1. **"Role of ROMO1 in mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation and apoptosis signaling"**
*Chung YM et al. (2011)*
摘要:研究利用特异性ROMO1抗体验证其在调控线粒体ROS生成中的作用,发现ROMO1通过激活NF-κB通路促进癌细胞凋亡抵抗,抗体用于Western blot和免疫荧光定位线粒体表达。
2. **"ROMO1 as a potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer progression"**
*Kim JH et al. (2015)*
摘要:通过抗ROMO1抗体检测结直肠癌组织中ROMO1高表达,证实其与患者预后不良相关,并揭示其通过ROS依赖的MAPK通路驱动肿瘤侵袭转移。
3. **"Development of a monoclonal antibody against human ROMO1 for oxidative stress studies"**
*Lee S et al. (2018)*
摘要:报道一种新型单克隆ROMO1抗体的开发与验证,应用于流式细胞术和免疫组化,证明其在神经退行性疾病模型中可定量检测氧化应激诱导的ROMO1上调。
---
注:以上为基于ROMO1已知功能的模拟文献,实际引用需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以“ROMO1 antibody”或“ROMO1 function”为关键词检索真实论文。
ROMO1 (Reactive Oxygen Modulator 1), also known as CCDC111 or HMO-Sh, is a mitochondrial membrane protein implicated in regulating reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and mitochondrial dynamics. First identified in 2005. it plays a critical role in maintaining mitochondrial membrane potential, apoptosis, and cellular stress responses. Dysregulation of ROMO1 is linked to various pathologies, including cancer progression, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders. Its overexpression has been observed in multiple cancers, where it promotes tumor growth and chemoresistance by enhancing ROS-mediated signaling pathways.
ROMO1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies (polyclonal or monoclonal) are typically developed against specific epitopes of human ROMO1 and validated for applications like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Researchers use them to investigate ROMO1's interaction partners, such as components of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, and its role in oxidative stress pathways. Recent studies also explore ROMO1 as a potential therapeutic target, driving demand for reliable antibodies in both diagnostic and drug development contexts. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity due to ROMO1's structural similarities with other mitochondrial proteins.
×