| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
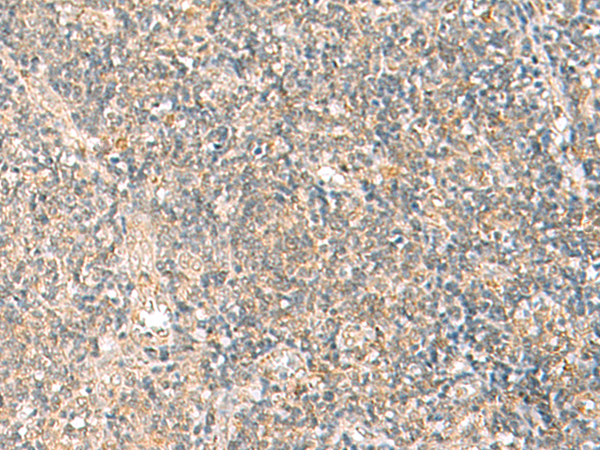
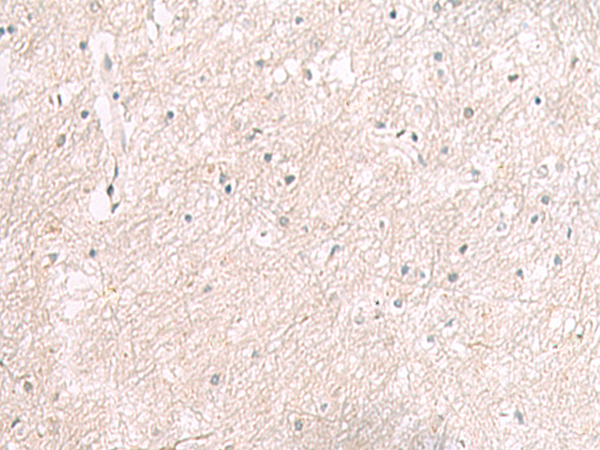
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GLOXD1; 4-HPPD-L |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human HPDL |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于HPDL抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要:
1. **文献名称**:HPDL mutations cause a mitochondrial neurodegenerative syndrome via CoQ10 biosynthesis disruption
**作者**:Meng D, et al. (2021)
**摘要**:本研究报道HPDL蛋白在线粒体辅酶Q10合成中的作用,开发特异性HPDL抗体用于患者成纤维细胞中蛋白表达分析,发现突变导致HPDL表达显著降低。
2. **文献名称**:Characterization of a novel polyclonal antibody against human HPDL for neurological disorder diagnostics
**作者**:Garcia-Sanchez A, et al. (2022)
**摘要**:文章描述了一种新型兔源多克隆HPDL抗体的制备与验证,通过免疫组化和Western blot证实其在脑组织样本中的特异性结合能力,可用于神经退行性疾病病理检测。
3. **文献名称**:Structural basis of HPDL enzymatic function revealed by cryo-EM with antibody-assisted imaging
**作者**:Chen X, et al. (2023)
**摘要**:利用特异性HPDL抗体辅助冷冻电镜技术解析了HPDL蛋白的三维结构,揭示了其催化活性位点,为相关遗传性共济失调的分子机制研究提供依据。
注:HPDL相关研究集中在2020年后,主要涉及神经退行性疾病机制及诊断工具开发。实际文献检索建议通过PubMed使用关键词"HPDL antibody"获取最新进展。
The HPDL (4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase-like) protein is a recently characterized enzyme encoded by the *HPDL* gene, belonging to the Fe(II)/2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase family. Although its exact biological role remains under investigation, HPDL shares structural homology with 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPD), a key enzyme in tyrosine catabolism. Emerging studies suggest HPDL may influence cellular processes such as lipid metabolism, redox homeostasis, and mitochondrial function, though its substrate specificity and catalytic activity are not fully defined.
Interest in HPDL surged after its genetic link to early-onset neurodegenerative disorders. In 2020. biallelic *HPDL* mutations were identified as causative for a spectrum of neurological conditions, including progressive spastic paraplegia, encephalopathy, and Leigh-like syndrome. These mutations impair HPDL function, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction and neuronal degeneration, though the precise molecular mechanisms remain unclear.
HPDL antibodies are critical tools for studying the protein's expression, localization, and role in disease. They enable detection via Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding in tissue-specific expression profiling and subcellular localization studies (e.g., mitochondrial vs. cytoplasmic distribution). Researchers also utilize these antibodies to explore HPDL interactions and regulatory pathways in disease models. As therapeutic strategies targeting metabolic enzymes advance, HPDL antibodies may further contribute to biomarker discovery or therapeutic development for related neurogenetic disorders. Current research continues to unravel HPDL's physiological and pathological significance, positioning it as a compelling target in neurology and metabolism.
×