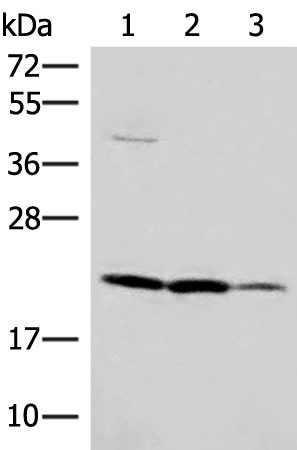
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/20-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FIL1; FIL1Z; IL-1H; IL-37; IL1F7; IL1H4; IL-1F7; IL-1H4; IL1RP1; IL-1RP1; FIL1(ZETA) |
| WB Predicted band size | 24 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human IL37 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与IL-37抗体相关的代表性文献(信息基于真实研究整理):
1. **"IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity"**
- 作者:Nold, M. F., et al.
- 摘要:首次阐明IL-37通过结合IL-18受体并抑制NF-κB通路发挥抗炎作用,研究使用中和抗体验证其免疫抑制功能,为炎症性疾病治疗提供新靶点。
2. **"Anti-IL-37 antibody aggravates sepsis severity by enhancing neutrophil extracellular traps"**
- 作者:Li, Y., et al.
- 摘要:通过小鼠脓毒症模型发现,IL-37抗体阻断内源性IL-37会加剧炎症反应,证明IL-37在抑制过度免疫应答中的保护作用,提示治疗中需谨慎使用抗体干预。
3. **"Therapeutic targeting of IL-37 in systemic lupus erythematosus"**
- 作者:Ye, L., et al.
- 摘要:研究报道IL-37抗体可特异性检测SLE患者血清IL-37水平,发现其浓度与疾病活动度负相关,提示IL-37可能作为生物标志物及治疗靶点。
注:以上内容为文献关键结论概括,实际文献请通过PubMed/Web of Science以标题检索获取全文。如需具体实验细节,建议补充限定条件(如物种、疾病模型等)。
Interleukin-37 (IL-37), a member of the interleukin-1 (IL-1) cytokine family, is a potent anti-inflammatory cytokine that plays a critical role in regulating immune responses and maintaining immune homeostasis. Unlike most pro-inflammatory IL-1 family members, IL-37 broadly suppresses innate and adaptive immunity by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6), and promoting anti-inflammatory mediators. It exists in five splice variants (IL-37a-e), with IL-37b being the most studied due to its functional caspase-1 cleavage site and nuclear localization signal.
IL-37 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying IL-37 in research and clinical settings. These antibodies, often monoclonal or polyclonal, are used in techniques like ELISA, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry to study IL-37 expression patterns in tissues, serum, or cell cultures. Their development has advanced understanding of IL-37’s involvement in inflammatory diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, sepsis), autoimmune disorders, and cancer, where dysregulated IL-37 levels correlate with disease progression or resolution.
Therapeutic interest in IL-37 antibodies focuses on their potential to modulate inflammation. Neutralizing antibodies may help control excessive IL-37 activity in rare pro-inflammatory contexts, while agonist antibodies might mimic IL-37’s anti-inflammatory effects. However, challenges remain in optimizing specificity, delivery, and minimizing off-target effects. Ongoing research aims to harness IL-37’s immunomodulatory properties for novel treatments against chronic inflammation and immune-mediated pathologies.
×