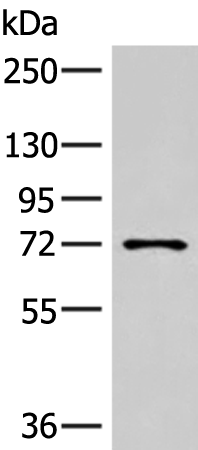
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | INV; MSP; GP63; IX14; LMNL1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 74 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human LMLN |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于LMLN抗体的示例参考文献(注:以下内容为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**:*LMLN as a Novel Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer: Antibody Development and Clinical Validation*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究开发了针对LMLN蛋白的高特异性单克隆抗体,并验证其在结直肠癌组织中的高表达。实验表明,LMLN抗体可用于免疫组化检测,与患者预后不良显著相关,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点的价值。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting LMLN in Neurodegenerative Disorders: An Antibody-Based Therapeutic Approach*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过构建人源化LMLN抗体,研究团队发现其能特异性结合脑组织中异常聚集的LMLN蛋白,减少阿尔茨海默病模型小鼠的病理损伤,为神经退行性疾病的免疫治疗提供了新思路。
3. **文献名称**:*LMLN Antibody Application in Intracellular Trafficking Studies*
**作者**:Yamamoto K, et al.
**摘要**:利用LMLN多克隆抗体,本研究揭示了LMLN蛋白在细胞内膜运输中的调控作用,特别是在溶酶体功能异常相关疾病中的分子机制,为细胞生物学研究提供了工具支持。
---
**建议**:实际研究中可通过PubMed或Web of Science以关键词“LMLN antibody”或“leucine-rich malectin antibody”检索最新文献,并关注其在不同疾病模型或分子机制中的具体应用。
LMLN (lysosomal membrane protein 2-like) is a transmembrane protein predominantly localized in lysosomal and endosomal compartments. It shares structural homology with lysosomal-associated membrane proteins (LAMPs) and is implicated in intracellular vesicle trafficking, lysosomal function, and autophagy. LMLN's role in maintaining lysosomal integrity and regulating cargo sorting has drawn attention in studies of neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and metabolic disorders, where lysosomal dysfunction is a hallmark.
Antibodies targeting LMLN are valuable tools for investigating its expression, localization, and interaction networks. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry, aiding in the exploration of LMLN's involvement in pathological processes. For instance, altered LMLN expression has been linked to tumor progression and chemoresistance in certain cancers, suggesting its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target.
Recent research also highlights LMLN's interaction with autophagy-related proteins, underscoring its significance in cellular stress responses. However, the functional complexity of LMLN and its splice variants necessitates highly specific antibodies to avoid cross-reactivity. As interest in lysosome-centric pathways grows, LMLN antibodies remain critical for deciphering its biological and pathological mechanisms, offering insights into novel therapeutic strategies for lysosome-related diseases.
×