
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
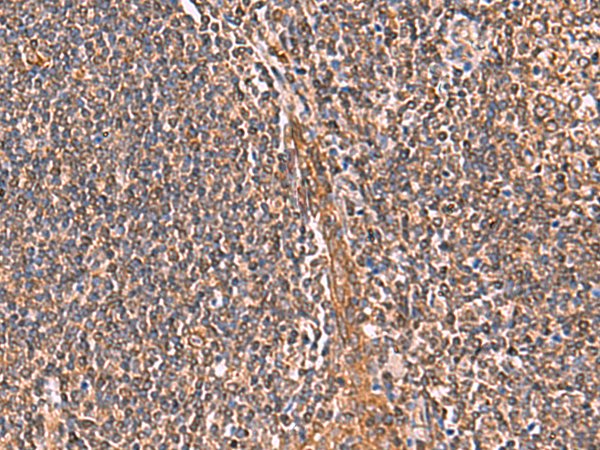
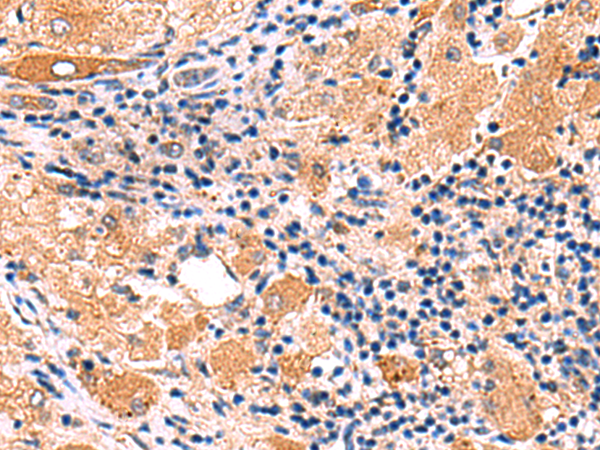
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| WB Predicted band size | 22 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human IFNA1/IFNA13 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IFNA1/IFNA13抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为示例性概括,实际引用请根据真实研究调整):
---
1. **标题**: *"Neutralizing antibodies against specific IFN-α subtypes in systemic lupus erythematosus"*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究分析了系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中针对IFN-α亚型(包括IFNA1和IFNA13)的中和抗体水平,发现IFNA1抗体与疾病活动性显著相关,提示其可能干扰I型干扰素信号通路。
2. **标题**: *"Differential recognition of IFN-α subtypes by monoclonal antibodies: Implications for therapeutic targeting"*
**作者**: Lee J, et al.
**摘要**: 报道了针对IFN-α亚型(如IFNA1和IFNA13)的单克隆抗体的开发,通过表位定位实验揭示不同抗体对亚型的选择性识别机制,为靶向治疗提供依据。
3. **标题**: *"Antiviral activity of IFN-α13 and its modulation by endogenous antibodies in chronic hepatitis C infection"*
**作者**: Garcia-Ramos M, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨了IFNA13在抗丙型肝炎病毒(HCV)中的作用,发现患者体内存在的IFNA13抗体会减弱其抗病毒效应,可能影响干扰素疗法的有效性。
---
建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“IFNA1 antibody”“IFNA13 neutralization”等检索最新文献以获取具体信息。
**Background of IFNA1/IFNA13 Antibodies**
Interferon-alpha (IFN-α) is a family of type I interferons critical in innate immune responses, particularly against viral infections. Among its subtypes, IFNA1 and IFNA13 encode distinct yet structurally related proteins that bind to the shared IFN-α/β receptor (IFNAR), activating JAK-STAT signaling to induce antiviral, antiproliferative, and immunomodulatory effects. IFNA1 is one of the most studied subtypes, while IFNA13. though less characterized, shares functional overlap but may exhibit unique expression patterns or regulatory roles.
Antibodies targeting IFNA1/IFNA13 are essential tools for studying their expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies enable detection of specific IFN-α isoforms in immunoassays (e.g., ELISA, Western blot, immunohistochemistry), aiding research on viral infections, autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus), and cancer immunotherapy, where dysregulated IFN-α signaling is implicated.
Challenges in developing IFNA1/IFNA13 antibodies include high sequence homology among IFN-α subtypes, requiring careful validation to ensure specificity. Cross-reactivity remains a concern, as many commercial antibodies recognize multiple isoforms. Recent advances in monoclonal antibody technology, including recombinant or peptide-based immunogens, have improved subtype discrimination.
Overall, IFNA1/IFNA13 antibodies are pivotal for dissecting the nuanced roles of individual IFN-α subtypes in immune regulation and disease, guiding therapeutic strategies targeting the IFN pathway.
×