| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
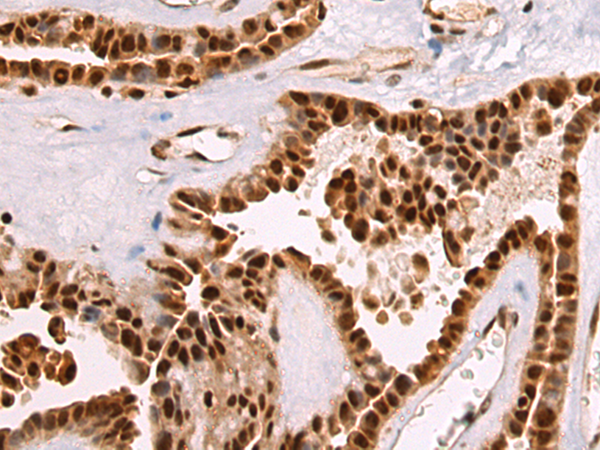
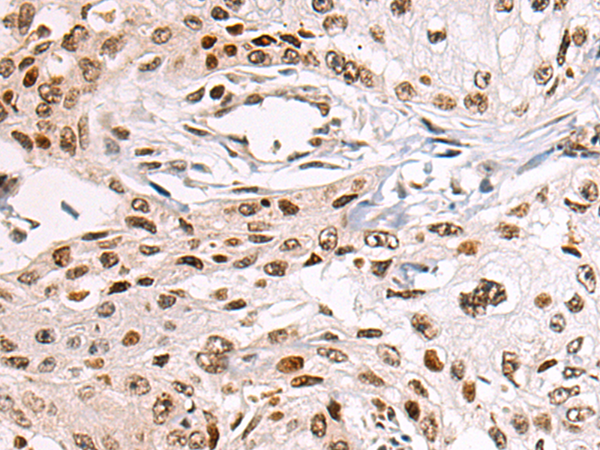
| IHC | 1/50-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CCD; AML3; CCD1; CLCD; OSF2; CBFA1; OSF-2; PEA2aA; PEBP2aA; CBF-alpha-1 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human RUNX2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于RUNX2抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者及摘要概括形式整理:
1. **文献名称**:*Targeted Disruption of Cbfa1 Results in a Complete Lack of Bone Formation owing to Maturational Arrest of Osteoblasts*
**作者**:Komori T. et al. (1997)
**摘要**:该研究通过基因敲除技术揭示RUNX2(Cbfa1)对成骨细胞分化的关键作用,并利用RUNX2抗体进行免疫组化分析,证实其在骨形成中的核心调控功能。
2. **文献名称**:*RUNX2 and Osteoblast Differentiation*
**作者**:Dalle Carbonare L. et al. (2009)
**摘要**:文章综述RUNX2在成骨分化中的分子机制,重点讨论了通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术使用RUNX2抗体检测其表达水平的方法,及其在骨质疏松症研究中的应用。
3. **文献名称**:*BMP-2-Induced Runx2 Expression is Mediated by Dlx5. and TGF-β1 Opposes the BMP-2-Induced Osteoblast Differentiation*
**作者**:Jeon M.J. et al. (2008)
**摘要**:研究利用RUNX2抗体在免疫沉淀和染色质免疫共沉淀(ChIP)中验证BMP-2信号通路对成骨分化的调控,揭示TGF-β1与BMP-2在成骨中的拮抗作用。
4. **文献名称**:*Cbfa1. a Candidate Gene for Cleidocranial Dysplasia Syndrome, is Essential for Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Development*
**作者**:Otto F. et al. (1997)
**摘要**:通过RUNX2抗体的免疫组化分析,证实Cbfa1(RUNX2)基因缺陷导致颅锁骨发育不全综合征,阐明其在骨骼发育中的必要性。
这些文献均涉及RUNX2抗体的实验应用(如Western blot、免疫组化、ChIP等),聚焦于其在成骨分化、骨骼疾病及信号通路机制研究中的作用。
The RUNX2 antibody is a crucial tool in biomedical research for studying the Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2), a master regulator of osteoblast differentiation and skeletal development. RUNX2. also known as core-binding factor subunit alpha-1 (CBFA1), plays a pivotal role in bone formation, chondrocyte maturation, and tooth development by controlling the expression of osteogenic genes like osteocalcin (BGLAP) and collagen type I alpha 1 (COL1A1). It contains a conserved Runt domain for DNA binding and protein interactions. Dysregulation of RUNX2 is implicated in skeletal disorders (e.g., cleidocranial dysplasia), metastatic bone diseases, and cancers, particularly osteosarcoma and breast/prostate cancer with bone metastasis.
Researchers use RUNX2 antibodies to detect and quantify RUNX2 protein levels in various applications, including Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). These antibodies help investigate RUNX2's nuclear localization, expression patterns during osteogenesis, and interactions with co-regulators like CBFβ. Commercial RUNX2 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal or C-terminal regions, and validated across species (human, mouse, rat). Recent studies also utilize RUNX2 antibodies to explore its non-skeletal roles in vascular calcification, immune regulation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Validation via knockout controls or siRNA knockdown remains essential due to potential cross-reactivity with other RUNX family members (RUNX1. RUNX3).
×