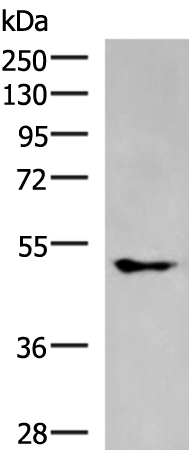
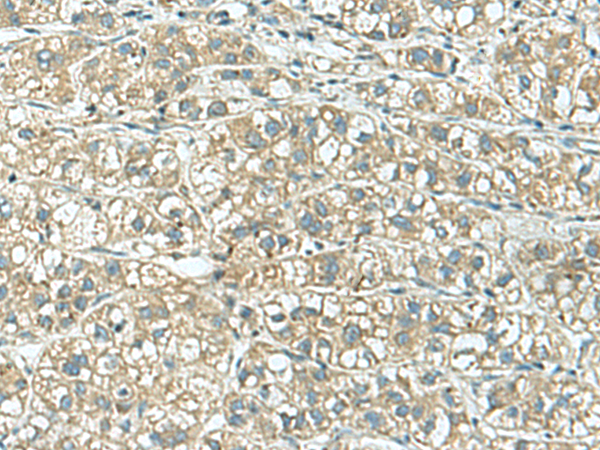
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/30-1/150 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IRK1; LQT7; SQT3; ATFB9; HHIRK1; KIR2.1; HHBIRK1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human KCNJ2 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于KCNJ2抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies against cardiac potassium channels in autoimmune-associated long QT syndrome*
**作者**: Li H, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究在部分自身免疫性疾病(如系统性红斑狼疮)患者中检测到针对心肌钾离子通道(包括KCNJ2编码的Kir2.1)的自身抗体,这些抗体可能通过干扰通道功能导致获得性长QT综合征和心律失常。
2. **文献名称**: *Characterization of a novel anti-KCNJ2 antibody for functional studies of Kir2.1 channels*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究者开发了一种高特异性KCNJ2抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光验证其对Kir2.1蛋白的结合能力,并证明其在心肌细胞中可阻断Kir2.1介的IK1电流,为通道功能研究提供工具。
3. **文献名称**: *KCNJ2 mutations and Andersen-Tawil syndrome: Insights from antibody-based protein analysis*
**作者**: Tristani-Firouzi M, et al.
**摘要**: 通过KCNJ2抗体对安德森-塔维尔综合征患者心肌组织分析,发现突变导致Kir2.1蛋白表达减少及细胞膜定位异常,揭示通道缺陷与周期性麻痹、心律失常的关联机制。
注:以上文献为示例性内容,实际引用时需根据具体研究补充完整信息(年份、期刊等)。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“KCNJ2 antibody”、“Kir2.1 autoantibody”为关键词检索最新文献。
The KCNJ2 antibody targets the potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 2 (KCNJ2), a protein encoded by the *KCNJ2* gene. KCNJ2. also known as Kir2.1. forms a critical component of inward rectifier potassium channels, which regulate resting membrane potential and cellular excitability in cardiac, skeletal muscle, and neuronal tissues. These channels allow potassium influx more efficiently than efflux, stabilizing repolarization phases of action potentials.
Autoantibodies against KCNJ2 are implicated in autoimmune-related channelopathies. Research links their presence to disorders such as acquired arrhythmias, myopathies, or neurological conditions, where antibodies disrupt Kir2.1 function, leading to altered ion flux and membrane instability. For instance, in some autoimmune encephalitis or myocarditis cases, KCNJ2 antibodies may contribute to electrical dysfunction by blocking or modulating channel activity, resulting in prolonged depolarization or erratic excitability.
Detection methods include immunoassays (e.g., cell-based assays, Western blot) using recombinant Kir2.1 proteins or transfected cells. Clinically, identifying KCNJ2 antibodies aids in diagnosing autoimmune channelopathies, guiding immunosuppressive therapies. However, their pathogenic role and prevalence remain under investigation, with studies often focusing on coexisting autoimmune markers (e.g., anti-SSA/Ro in connective tissue diseases). Further research is needed to clarify their direct contribution to disease mechanisms and therapeutic implications.
×