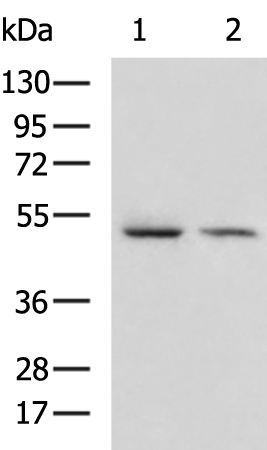
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
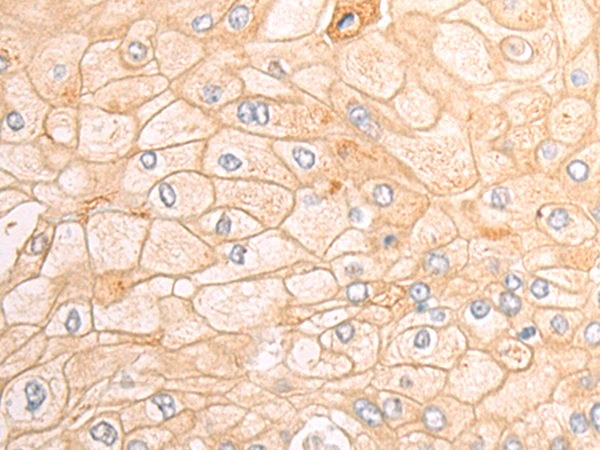
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B7-H; B7H1; PDL1; PD-L1; hPD-L1; PDCD1L1; PDCD1LG1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human CD274 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CD274(PD-L1)抗体的3篇代表性文献的简要总结:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Atezolizumab versus Docetaxel in Patients with Previously Treated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (OAK)*
**作者**:Rittmeyer A, et al.
**摘要**:该III期临床试验(OAK研究)评估了抗PD-L1抗体Atezolizumab在晚期非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)二线治疗中的疗效。结果显示,与多西他赛化疗相比,Atezolizumab显著延长患者总生存期(OS),且疗效与PD-L1表达水平相关,为免疫治疗在NSCLC中的应用提供了关键证据。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer*
**作者**:Antonia SJ, et al.
**摘要**:PACIFIC临床试验表明,针对PD-L1的抗体Durvalumab作为III期不可切除NSCLC患者放化疗后的维持治疗,可显著延长无进展生存期(PFS)和总生存期(OS)。研究强调了免疫治疗在巩固治疗中的作用,并推动Durvalumab成为该阶段患者的标准疗法。
---
3. **文献名称**:*PD-L1 as a Biomarker of Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors*
**作者**:Topalian SL, et al.
**摘要**:该综述探讨了PD-L1表达作为免疫检查点抑制剂疗效预测标志物的临床意义。作者总结了PD-L1检测方法的标准化挑战,并指出其在不同肿瘤类型中的异质性,强调需结合其他生物标志物(如肿瘤突变负荷)以提高预测准确性。
---
如需更多文献或特定研究方向,可进一步补充说明。
CD274. also known as programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1), is a transmembrane protein belonging to the B7 family of immune checkpoint molecules. It is primarily expressed on antigen-presenting cells and certain tumor cells, where it interacts with the PD-1 receptor on T cells to suppress immune activation. By binding PD-1. CD274/PD-L1 delivers inhibitory signals that dampen T-cell proliferation, cytokine production, and cytotoxic activity, enabling tumors to evade immune surveillance. This mechanism has made CD274 a critical target in cancer immunotherapy.
Anti-CD274 antibodies are monoclonal antibodies designed to block the PD-1/PD-L1 interaction, thereby restoring T-cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Clinically, these antibodies, such as atezolizumab, avelumab, and durvalumab, are used to treat various cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer, bladder cancer, and melanoma. Their efficacy often correlates with PD-L1 expression levels in tumors, though responses can vary due to tumor microenvironment complexity.
Beyond oncology, CD274 antibodies are explored in infectious and autoimmune diseases, reflecting the protein’s role in modulating immune tolerance. Challenges include managing immune-related adverse events and optimizing patient stratification. Overall, CD274 antibodies represent a transformative approach in immunotherapy, leveraging immune checkpoint blockade to enhance anticancer responses.
×