| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NS; NS3; OES; CFC2; RALD; K-Ras; KRAS1; KRAS2; RASK2; KI-RAS; C-K-RAS; K-RAS2A; K-RAS2B; K-RAS4A; K-RAS4B; K-Ras 2; 'C-K-RAS; c-Ki-ras; c-Ki-ras2 |
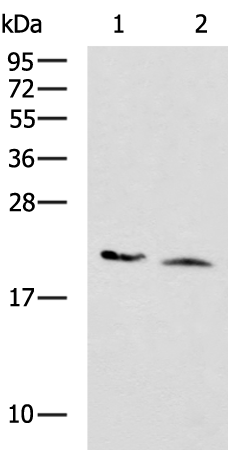
| WB Predicted band size | 22 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide of human KRAS |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3-4篇关于KRAS抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS by a conformational antibody that disrupts effector binding*
**作者**:Zimmermann, G. et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种构象特异性单克隆抗体,可选择性结合活性状态的突变KRAS(如G12V和G12D),阻断其与RAF等效应蛋白的相互作用,抑制下游MAPK信号通路,并在胰腺癌小鼠模型中展示抗肿瘤活性。
2. **文献名称**:*A bispecific antibody approach for targeting mutant KRAS-driven cancers*
**作者**:Tong, Y. et al.
**摘要**:研究者设计了一种双特异性抗体,同时靶向突变KRAS蛋白和细胞表面受体EGFR,增强对结直肠癌和肺癌细胞的结合特异性,抑制肿瘤生长并克服单靶点治疗的耐药性。
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-mediated delivery of a KRAS inhibitor in pancreatic cancer models*
**作者**:Lim, S. et al.
**摘要**:通过抗体-药物偶联物(ADC)技术,将小分子KRAS抑制剂特异性递送至KRAS突变型胰腺癌细胞,减少脱靶毒性,并在临床前模型中显著抑制肿瘤进展。
4. **文献名称**:*Challenges and opportunities in targeting KRAS with antibodies*
**作者**:Singh, H. et al.
**摘要**:综述性文章,系统讨论了开发KRAS抗体的难点(如蛋白表面平滑、缺乏明确表位),以及新兴策略(如纳米抗体、表位定向筛选),展望了联合疗法和精准递送系统的前景。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例性概括,实际文献可能存在差异。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar使用关键词(如“KRAS antibody therapy”)获取最新准确信息。
The KRAS protein, encoded by the KRAS gene, is a critical signaling molecule in the Ras/MAPK pathway, regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Mutations in KRAS are among the most common oncogenic drivers, occurring in ~25% of human cancers, including pancreatic, colorectal, and lung adenocarcinomas. These mutations (e.g., G12D, G12V, G13D) lock KRAS in a constitutively active GTP-bound state, promoting uncontrolled cell growth. For decades, KRAS was deemed "undruggable" due to its smooth surface, high GTP affinity, and lack of deep binding pockets for small molecules.
Antibody-based targeting of KRAS faced similar challenges. Traditional monoclonal antibodies struggled to block KRAS activity directly, as intracellular localization limited accessibility. However, advances in antibody engineering, including nanobodies, bispecific formats, and covalent binders, have enabled novel approaches. For example, allele-specific antibodies targeting mutant KRAS (e.g., anti-KRAS G12D) exploit unique neoantigenic epitopes, offering precision in distinguishing mutated from wild-type proteins. Others inhibit KRAS-effector interactions or target KRAS membrane localization by disrupting its interaction with PDEδ.
KRAS antibodies also serve as diagnostic tools, detecting mutation status in tumors via IHC or liquid biopsies. While no KRAS-targeting antibody has yet gained clinical approval, preclinical models show promise, particularly in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors or RAS pathway inhibitors. Ongoing research focuses on improving delivery, specificity, and overcoming resistance mechanisms.
×