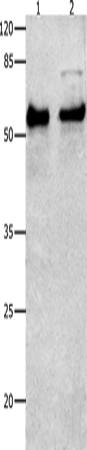
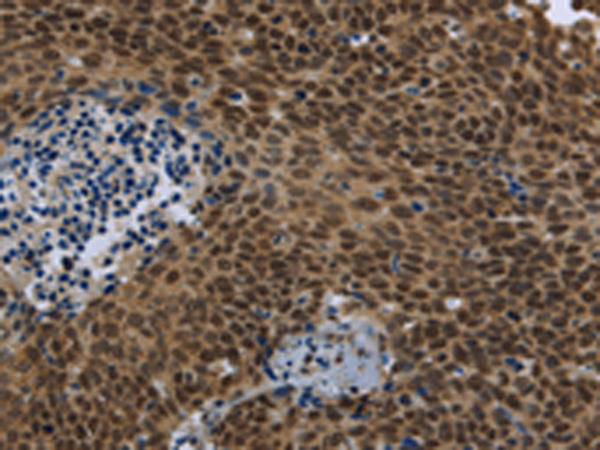
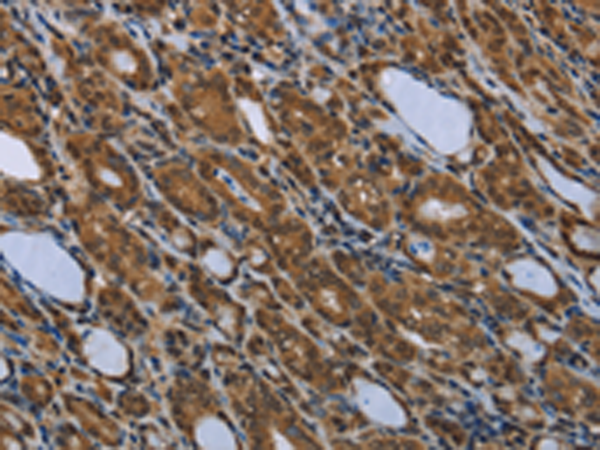
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | JIP, DPC4, MADH4, MYHRS |
| WB Predicted band size | 60 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human SMAD4 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于SMAD4抗体的参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"SMAD4 Loss in Colorectal Cancer Induces Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy via FGFR/PI3K/AKT Signaling Activation"*
**作者**: Lannagan, T.R.M. et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过免疫组化(使用SMAD4抗体)和基因测序分析结直肠癌中SMAD4蛋白缺失与抗EGFR治疗耐药性的关联,发现SMAD4缺失通过激活FGFR/PI3K/AKT通路促进耐药性。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Validation of a Novel SMAD4 Antibody for Immunohistochemical Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma"*
**作者**: Shi, C. et al.
**摘要**: 验证一种高特异性SMAD4抗体在胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)诊断中的应用,证明其可有效检测肿瘤组织中的SMAD4蛋白缺失,并辅助区分PDAC与其他胰腺病变。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"SMAD4 Mutations and Protein Expression in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia"*
**作者**: Tillet, E. et al.
**摘要**: 利用Western blot和免疫荧光(基于SMAD4抗体)研究遗传性出血性毛细血管扩张症(HHT)患者的SMAD4突变对蛋白表达的影响,发现突变导致SMAD4核转位异常,破坏TGF-β信号传导。
---
4. **文献名称**: *"Differential Roles of SMAD4 in TGF-β-Dependent and Inflammatory Pathways in Cancer"*
**作者**: Xu, P. et al.
**摘要**: 通过多种抗体(包括SMAD4)的对比实验,揭示SMAD4在TGF-β信号通路与炎症相关癌症进展中的双重作用,强调其在肿瘤微环境调控中的复杂性。
---
以上文献均涉及SMAD4抗体的实验应用(如免疫组化、Western blot),涵盖癌症机制、诊断及遗传疾病研究。
The SMAD4 antibody is a crucial tool in studying the SMAD4 protein, a central mediator of the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) signaling pathway. SMAD4. also known as DPC4 (Deleted in Pancreatic Carcinoma 4), functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating gene expression in response to TGF-β signals. It forms complexes with receptor-activated SMADs (SMAD1/5/8 or SMAD2/3) to translocate into the nucleus, where it modulates transcription of target genes involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, and immune responses. Dysregulation of SMAD4 is linked to various cancers, particularly pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), colorectal cancer, and juvenile polyposis syndrome, where SMAD4 mutations or loss of expression correlate with disease progression and poor prognosis.
SMAD4 antibodies are widely used in research to detect protein expression, localization, and post-translational modifications via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF). These antibodies help elucidate SMAD4's role in tumor suppression, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and TGF-β signaling crosstalk with other pathways. Commercial SMAD4 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, with validation in knockout cell lines to ensure specificity. Clinically, SMAD4 IHC aids in diagnosing SMAD4-deficient tumors and hereditary conditions like hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) or juvenile polyposis syndrome. However, variability in antibody performance across tissue types and fixation methods necessitates careful experimental optimization. Ongoing research continues to refine SMAD4 antibody applications in both mechanistic studies and biomarker development.
×