| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
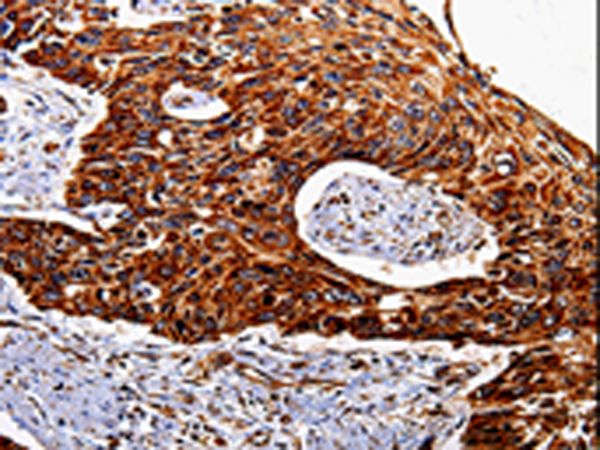
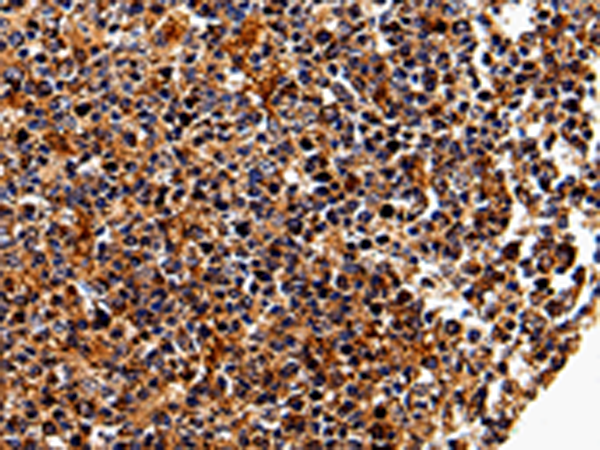
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL17RL |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human IL17RC |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL17RC抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Structural basis of receptor sharing by interleukin 17 cytokines"*
**作者**: Ely, L.K., et al.
**摘要**: 该研究解析了IL-17A与IL-17RC/IL-17RA受体复合物的晶体结构,揭示了IL-17RC在信号传导中的关键作用,为开发靶向IL17RC的抗体药物提供了结构基础。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Anti-IL-17 receptor antibody ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice"*
**作者**: Song, X., et al.
**摘要**: 通过小鼠银屑病模型,证明抗IL17RC抗体可阻断IL-17A和IL-17F信号通路,显著减轻皮肤炎症和病理损伤,提示其在治疗自身免疫疾病中的潜力。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"IL-17RC: A partner in crime with IL-17 in autoimmunity and infection?"*
**作者**: Gaffen, S.L., et al.
**摘要**: 综述了IL17RC在IL-17信号通路中的核心功能,探讨其抗体在抑制炎症反应(如类风湿性关节炎和真菌感染)中的治疗机制及临床前研究进展。
---
如需更多文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“IL17RC antibody”为关键词进一步检索。
Interleukin-17 receptor C (IL-17RC), a key component of the IL-17 receptor family, plays a critical role in mediating inflammatory and autoimmune responses. It forms a heterodimeric complex with IL-17RA, serving as the functional receptor for IL-17A and IL-17F, cytokines central to host defense and pathological inflammation. IL-17RC is expressed on epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and immune cells, where its activation triggers downstream signaling pathways, including NF-κB and MAPK, promoting the production of pro-inflammatory mediators like chemokines and antimicrobial peptides. Dysregulation of the IL-17/IL-17RC axis is implicated in autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
IL-17RC-targeting antibodies have emerged as therapeutic tools to modulate this pathway. These antibodies typically function by blocking IL-17A/F binding to IL-17RC, thereby inhibiting receptor activation and subsequent inflammatory cascades. Preclinical studies demonstrate their efficacy in reducing disease severity in animal models of psoriasis and arthritis. Clinical development has focused on autoimmune conditions, with some candidates progressing to early-phase trials. Challenges include optimizing receptor specificity to minimize off-target effects and balancing immunosuppression with infection risks. Research also explores diagnostic applications, as IL-17RC expression levels may correlate with disease activity. As understanding of IL-17RC's structural interactions grows, next-generation antibodies aim to achieve enhanced affinity and tailored pharmacokinetics, offering potential for personalized therapies in IL-17-driven disorders.
×