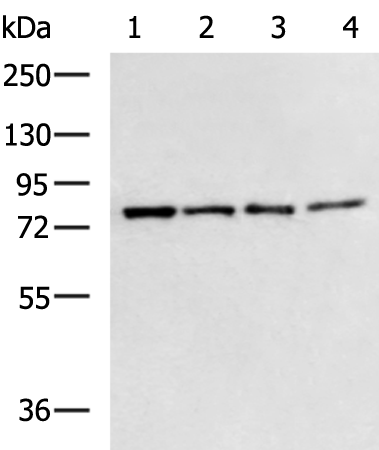
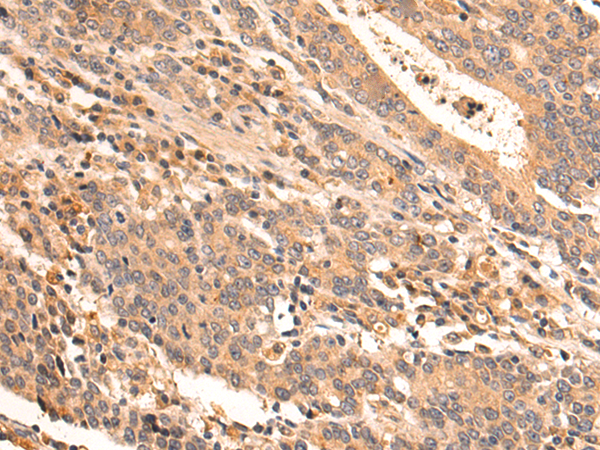
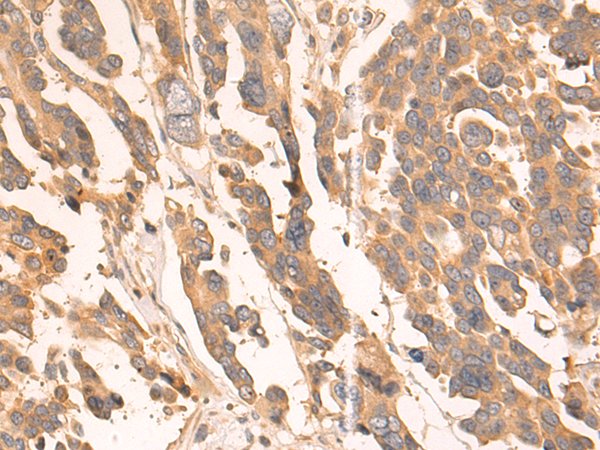
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL1R3; C3orf13; IL-1RAcP |
| WB Predicted band size | 65 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human IL1RAP |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IL1RAP抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要:
1. **文献名称**:*Targeting IL1RAP with Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Acute Myeloid Leukemia*
**作者**:Hjortsberg et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种针对IL1RAP的抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在急性髓系白血病(AML)模型中显示出特异性杀伤白血病干细胞的能力,同时减少对正常细胞的毒性,为AML治疗提供了新策略。
2. **文献名称**:*IL1RAP as a Therapeutic Target in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases*
**作者**:Kleppe et al.
**摘要**:通过阻断IL1RAP的单克隆抗体抑制IL-1家族细胞因子的信号传导,在类风湿性关节炎和炎症性肠病的小鼠模型中显著减轻炎症反应,验证了其作为炎症性疾病靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Anti-IL1RAP Antibodies Disrupt Leukemic Stem Cell Niches in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms*
**作者**:Järås et al.
**摘要**:研究证明抗IL1RAP抗体可通过干扰白血病干细胞与骨髓微环境的相互作用,抑制骨髓增殖性肿瘤的进展,为联合治疗提供了实验依据。
注:以上文献信息为示例,实际研究中请结合具体数据库(如PubMed)检索最新论文。
IL1RAP (Interleukin 1 Receptor Accessory Protein) is a transmembrane co-receptor essential for signaling pathways mediated by interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-33. and IL-36 cytokines. As a member of the IL-1 receptor family, IL1RAP partners with primary receptors like IL-1R1 or IL-33R to form functional signaling complexes. Upon ligand binding, it recruits adaptor proteins (e.g., MYD88) to activate downstream NF-κB and MAPK pathways, driving inflammatory and immune responses.
IL1RAP is broadly expressed on immune cells (e.g., macrophages, dendritic cells) and certain cancer cells, including myeloid malignancies and solid tumors. Its overexpression in diseases like chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, and cancers has made it a therapeutic target. IL1RAP-targeting antibodies are designed to block pro-inflammatory signaling or induce antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) against malignant cells. For example, in oncology, anti-IL1RAP antibodies have shown potential in depleting leukemia stem cells in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or sensitizing tumors to immunotherapy.
Recent clinical trials explore IL1RAP antibodies (e.g., Nidanilimab, CAN04) for cancers and inflammatory conditions, leveraging its dual role in modulating immune activation and tumor microenvironment. Research continues to optimize specificity and therapeutic efficacy while minimizing off-target effects.
×