
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
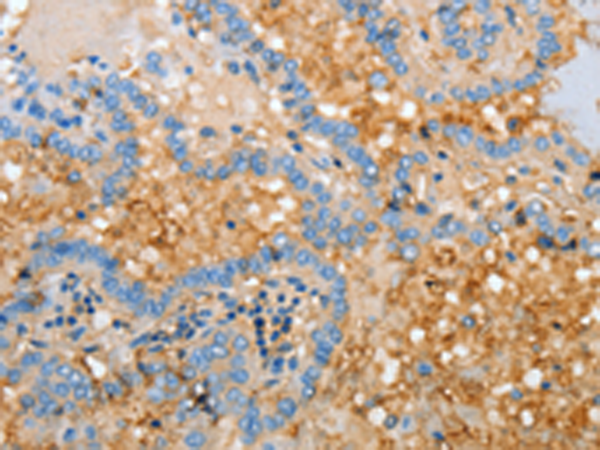
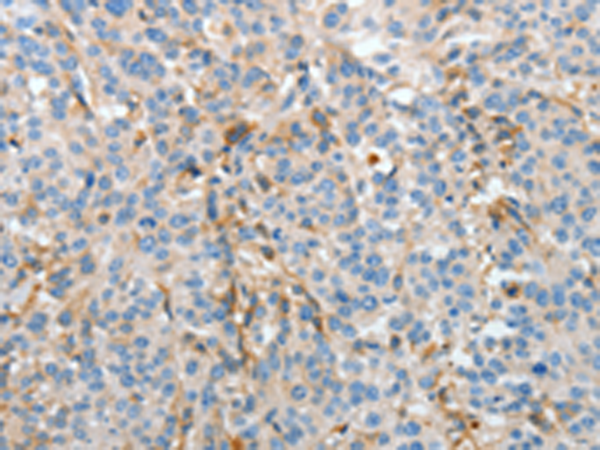
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BG; B2G1; B2GP1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 38 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human APOH |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于APOH(β2糖蛋白I)抗体的3篇代表性文献,信息基于公开研究总结:
1. **《Anti-β2-glycoprotein I autoantibodies: from pathogenesis to clinical implications》**
*作者:Pierangeli SS, et al. (2008)*
摘要:探讨APOH抗体在抗磷脂综合征(APS)中的致病机制,包括与血栓形成和妊娠并发症的关联,强调其通过干扰凝血系统导致病理表现。
2. **《The role of β2-glycoprotein I in the antiphospholipid syndrome》**
*作者:de Groot PG, et al. (2011)*
摘要:分析β2糖蛋白I的结构功能及其与APOH抗体的相互作用,揭示该抗体如何破坏细胞膜稳态并促进血栓形成,为临床诊断标志物提供依据。
3. **《Laboratory criteria for antiphospholipid syndrome: Where are we now?》**
*作者:Devreese KMJ, et al. (2020)*
摘要:综述APOH抗体在APS实验室诊断中的标准化检测方法(如ELISA),讨论其敏感性和特异性,以及与其他抗磷脂抗体的临床区分价值。
4. **《Pathogenic mechanisms of anti-β2-glycoprotein I antibodies in antiphospholipid syndrome》**
*作者:Agmon-Levin N, et al. (2010)*
摘要:总结APOH抗体通过激活内皮细胞、补体系统和血小板促进血栓形成的分子机制,并提出靶向治疗的研究方向。
*注:以上文献信息为领域内经典或高引研究内容的概括,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或期刊官网核对原文细节。*
APOH antibodies, also called anti-β2-glycoprotein I (β2GPI) antibodies, are autoantibodies targeting apolipoprotein H (APOH), a plasma protein involved in lipid metabolism and blood clotting regulation. Discovered in the 1990s, these antibodies are strongly associated with antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), a disorder characterized by recurrent thrombosis, pregnancy complications, and persistent antiphospholipid antibodies. Unlike antibodies to cardiolipin or lupus anticoagulants, APOH antibodies specifically recognize epitopes on β2GPI, a cofactor required for binding anionic phospholipids.
In APS, APOH antibodies disrupt β2GPI’s anticoagulant function by forming immune complexes that activate endothelial cells, platelets, and complement pathways, promoting thrombosis. They are considered more specific than other antiphospholipid antibodies for diagnosing APS, particularly in thrombotic events and obstetric complications like recurrent miscarriages. Elevated APOH antibodies are also observed in autoimmune diseases (e.g., SLE) and infections, though transiently. Testing involves ELISA, with IgG/IgM isotypes having higher clinical relevance. Research continues to explore their pathogenic mechanisms, including interactions with coagulation factors and cellular receptors, to improve diagnostic accuracy and targeted therapies.
×