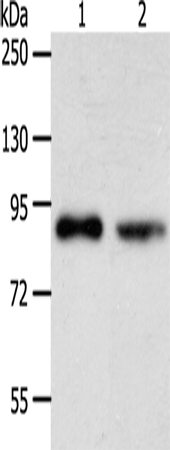
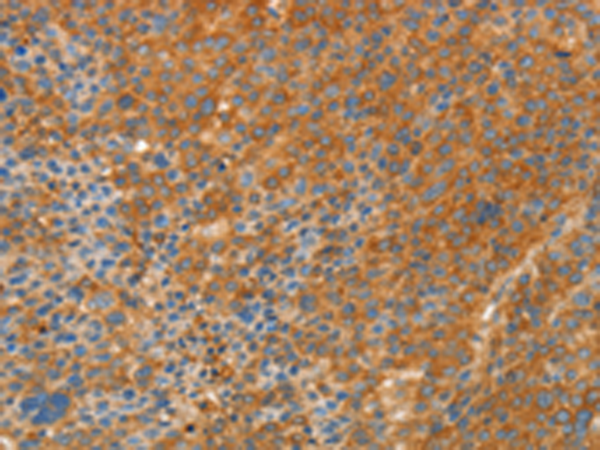
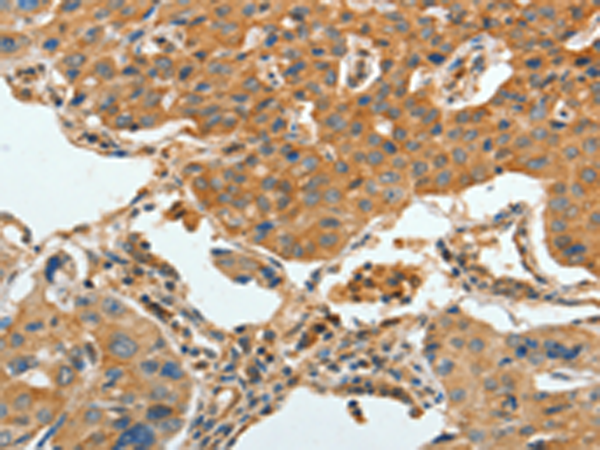
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | APPL; DIP13alpha |
| WB Predicted band size | 80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human APPL1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及APPL1抗体的研究文献及其摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*APPL proteins link Rab5 to nuclear signal transduction via an endosomal compartment*
**作者**:Schenck A. et al. (2008)
**摘要**:该研究利用APPL1抗体通过免疫共沉淀和免疫荧光技术,揭示了APPL1作为Rab5效应蛋白,在早期内体介导的细胞核信号转导中的作用,证明其参与生长因子诱导的AKT信号通路调控。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Role of APPL1 in autophagy regulation via interaction with Beclin-1*
**作者**:Park S. et al. (2013)
**摘要**:通过Western blot和共聚焦显微镜结合APPL1抗体,研究发现APPL1通过与自噬关键蛋白Beclin-1相互作用调控自噬体形成,在营养缺乏条件下增强细胞自噬活性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*APPL1 potentiates insulin-mediated inhibition of hepatic glucose production*
**作者**:Xin X. et al. (2011)
**摘要**:利用APPL1抗体进行组织免疫染色和蛋白质分析,发现APPL1在肝脏中通过增强胰岛素受体信号通路抑制糖异生,为2型糖尿病治疗提供了潜在靶点。
---
这些文献展示了APPL1抗体在信号通路解析、细胞器功能研究及代谢疾病机制中的典型应用。如需更多文献细节,可进一步提供方向或PMID编号。
APPL1 (Adaptor Protein containing PH domain, PTB domain, and Leucine zipper motif 1) is a multifunctional adaptor protein involved in diverse cellular processes, including signal transduction, membrane trafficking, and organelle crosstalk. It interacts with various signaling molecules, such as AKT, Rab5. and Ras family proteins, and plays critical roles in regulating insulin signaling, energy metabolism, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. APPL1 is localized to endosomes, mitochondria, and the nucleus, acting as a scaffold to mediate cross-talk between pathways like the PI3K/AKT and AMPK pathways. Dysregulation of APPL1 has been linked to metabolic disorders (e.g., diabetes, obesity), cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases.
APPL1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence to investigate APPL1's role in cellular processes. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies targeting specific domains (e.g., N-terminal or C-terminal regions) enable researchers to probe conformational changes or post-translational modifications. Validated APPL1 antibodies often undergo knockout cell line testing to ensure specificity. These reagents are critical for exploring APPL1's involvement in disease mechanisms, therapeutic target identification, and biomarker discovery. Commercial APPL1 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with applications spanning basic research, drug development, and clinical diagnostics.
×