
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
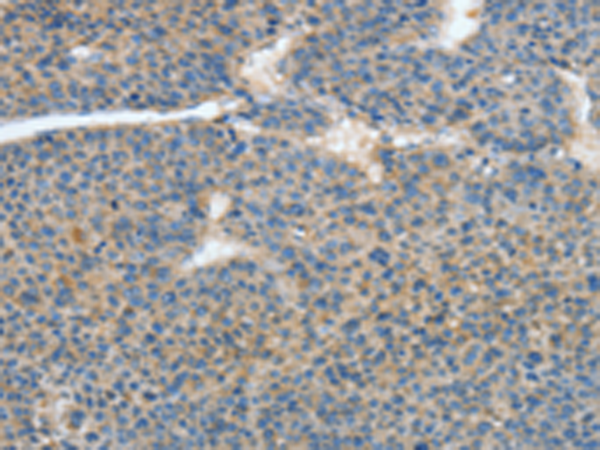
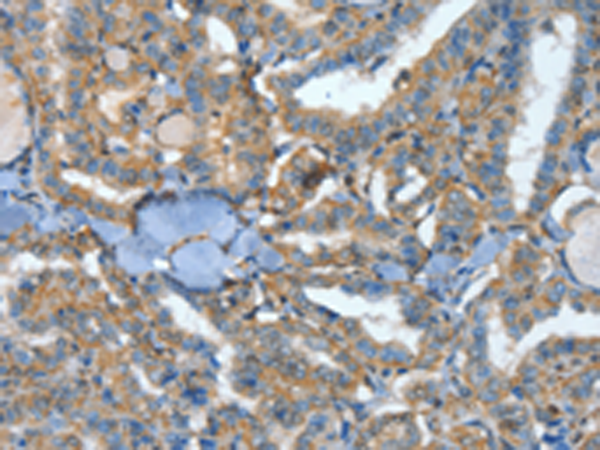
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ATP6B |
| WB Predicted band size | 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ATP4B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ATP4B抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**: "Autoantibodies to the gastric H+/K+-ATPase in autoimmune gastritis"
**作者**: Toh BH, Gleeson PA
**摘要**: 该研究探讨了针对胃H+/K+-ATP酶(ATP4B为β亚基)的自身抗体在自身免疫性胃炎中的意义,发现其与胃黏膜萎缩和恶性贫血密切相关,提示其可作为疾病诊断的生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**: "Molecular mimicry between Helicobacter pylori and gastric mucosa: implications for autoimmunity"
**作者**: Appelmelk BJ, Negrini R
**摘要**: 文章分析了幽门螺杆菌感染与自身免疫性胃炎的关系,提出H. pylori抗原与ATP4B存在分子模拟现象,可能导致交叉反应性抗体的产生,进而引发胃黏膜损伤。
3. **文献名称**: "Diagnostic value of anti-ATP4B antibodies in autoimmune gastritis"
**作者**: Claeys D, Faller G
**摘要**: 研究评估了ATP4B抗体检测在自身免疫性胃炎中的敏感性和特异性,发现其与内镜及组织学结果高度一致,建议作为非侵入性辅助诊断工具。
4. **文献名称**: "Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the β-subunit of H+/K+-ATPase"
**作者**: Strugala V, Dettmar PW
**摘要**: 通过制备抗ATP4B的单克隆抗体,揭示了该亚基的表位分布及其在胃酸分泌调控中的作用,为后续病理机制研究提供了工具。
以上文献涵盖ATP4B抗体的致病机制、诊断价值及实验工具开发,均发表于1990-2000年代的核心期刊(如*Autoimmunity*、*Gastroenterology*等)。
The ATP4B antibody targets the beta subunit of the gastric H+/K+ ATPase, a proton pump critical for acid secretion in parietal cells of the stomach. This enzyme exchanges cytoplasmic H+ ions for luminal K+ ions, generating the highly acidic gastric environment necessary for digestion. ATP4B antibodies are primarily associated with autoimmune gastritis, a chronic inflammatory condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks gastric parietal cells. Their presence often correlates with the destruction of acid-producing cells, leading to hypochlorhydria (reduced stomach acid) and impaired absorption of nutrients like vitamin B12. which may progress to pernicious anemia.
These antibodies are detected in approximately 50–70% of autoimmune gastritis cases and are frequently observed alongside ATP4A (alpha subunit) antibodies. Clinically, ATP4B antibody testing aids in diagnosing autoimmune gastritis, distinguishing it from other forms of gastritis or anemia. They are also linked to autoimmune polyendocrine syndromes, coexisting with other autoantibodies (e.g., thyroid or pancreatic islet cell antibodies). Detection methods include immunoassays (ELISA, Western blot) or indirect immunofluorescence. While not exclusive to autoimmune gastritis, their presence supports a diagnosis when combined with clinical symptoms, histopathology, and biomarkers like elevated gastrin or low pepsinogen levels. Research continues to explore their pathogenic role and utility in monitoring disease progression.
×