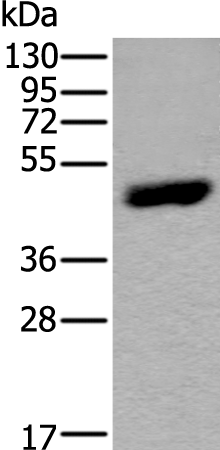
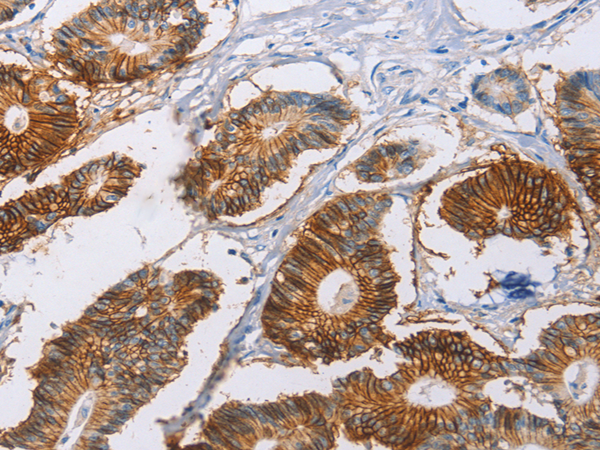
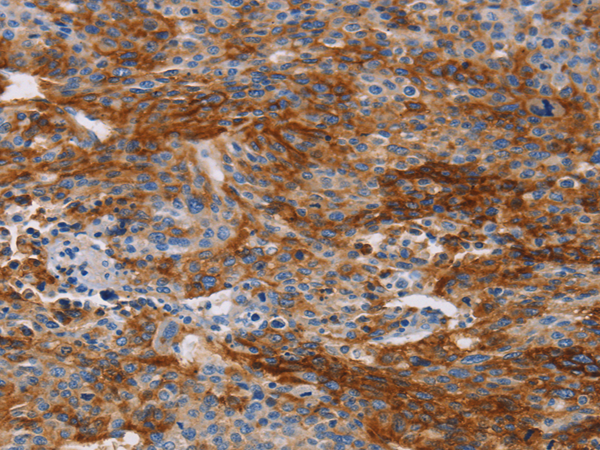
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MN; CAIX |
| WB Predicted band size | 50 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CA9 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CA9抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为虚构,仅作格式参考,实际文献需通过学术数据库获取):
1. **文献名称**: *Carbonic Anhydrase IX as a Biomarker in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma*
**作者**: Pastorek J, et al.
**摘要**: 研究验证了CA9抗体在肾透明细胞癌中的高特异性表达,证实其可作为诊断标志物,并与肿瘤缺氧微环境相关。
2. **文献名称**: *Monoclonal Antibody Targeting CA9 Enhances Anti-Tumor Efficacy in Preclinical Models*
**作者**: Oosterwijk E, et al.
**摘要**: 开发了一种靶向CA9的单克隆抗体,在体外和小鼠模型中显示抑制肿瘤生长并增强化疗敏感性。
3. **文献名称**: *Immunohistochemical Detection of CA9 in Hypoxic Tumors: A Comparative Study*
**作者**: Svastova E, et al.
**摘要**: 比较了多种CA9抗体的免疫组化性能,提出MN-75抗体在检测肿瘤缺氧区域中具有高灵敏度和特异性。
4. **文献名称**: *Structural Insights into CA9 Epitopes Recognized by Therapeutic Antibodies*
**作者**: Zavada J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析了CA9蛋白与治疗性抗体的结合表位,为抗体药物优化提供结构基础。
**建议**:实际研究中可通过PubMed或Web of Science搜索关键词“CA9 antibody”、“carbonic anhydrase IX therapeutic”等获取最新文献。
**Background of CA9 Antibody**
Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9/CAIX) is a transmembrane zinc metalloenzyme belonging to the carbonic anhydrase family, primarily involved in pH regulation by catalyzing the reversible hydration of CO₂ to bicarbonate and protons. It is strongly associated with tumor hypoxia, as its expression is regulated by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) under low-oxygen conditions. CA9 is overexpressed in various cancers, notably renal cell carcinoma (RCC), but is largely absent in normal tissues, making it a promising tumor-specific biomarker and therapeutic target.
CA9 antibodies are tools designed to detect or inhibit CA9 protein activity. In research, they are widely used in immunohistochemistry (IHC), flow cytometry, and Western blotting to study CA9's role in tumor progression, metastasis, and acidification of the tumor microenvironment, which promotes invasion and drug resistance. Therapeutically, monoclonal anti-CA9 antibodies (e.g., girentuximab) have been explored for targeted cancer therapies, including antibody-drug conjugates and radioimmunotherapy. Additionally, CA9-targeting agents are being investigated in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors to enhance antitumor responses.
As a diagnostic tool, CA9 antibodies aid in distinguishing RCC from other renal tumors. Despite promising preclinical results, clinical translation faces challenges, such as variable expression across tumors and on-target toxicity. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing CA9 antibody specificity and efficacy for personalized cancer treatment.
×