
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
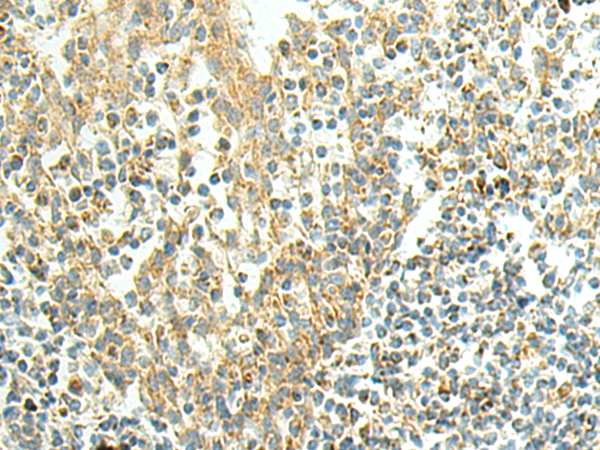
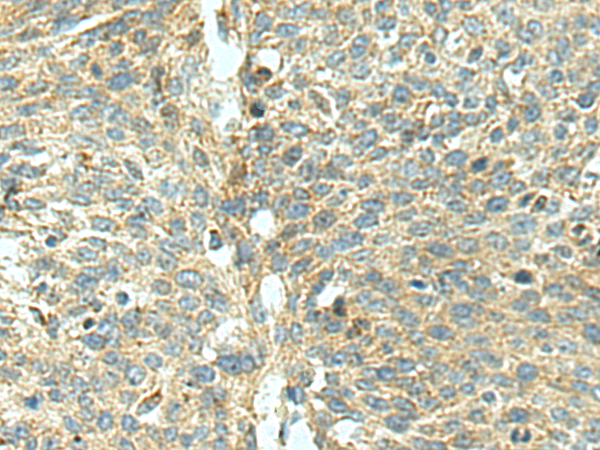
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | BGR; CD369; CANDF4; SCARE2; DECTIN1; CLECSF12 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CLEC7A |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CLEC7A抗体的3篇文献概览:
1. **"Dectin-1 mediates the biological effects of β-glucans"**
- **作者**: Brown, G.D. et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究揭示CLEC7A(Dectin-1)作为β-葡聚糖的关键受体,通过其抗体阻断实验证明其在巨噬细胞抗真菌免疫应答中的核心作用,包括促炎细胞因子释放和吞噬作用调控。
2. **"Targeting CLEC7A in cancer immunotherapy enhances dendritic cell activation"**
- **作者**: LeibundGut-Landmann, S. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用CLEC7A特异性抗体激活树突状细胞内的Syk信号通路,增强抗原呈递和T细胞抗肿瘤反应,为癌症免疫治疗提供新策略。
3. **"Anti-CLEC7A antibodies modulate autoimmune inflammation via NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition"**
- **作者**: Gringhuis, S.I. et al.
- **摘要**: 通过动物模型证明,阻断CLEC7A抗体可抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化,减轻类风湿性关节炎等自身免疫疾病的炎症损伤,提示其治疗潜力。
4. **"CLEC7A antibody-based glycan recognition directs Th17 differentiation in mucosal immunity"**
- **作者**: Taylor, P.R. et al.
- **摘要**: 该文献阐明CLEC7A抗体如何通过识别特定病原体多糖结构,调控肠道黏膜中Th17细胞分化,影响宿主对细菌感染的免疫防御机制。
注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献需通过学术数据库(如PubMed)检索确认。
CLEC7A (C-type lectin domain containing 7A), also known as Dectin-1. is a transmembrane C-type lectin receptor primarily expressed on myeloid cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils. It plays a critical role in innate immunity by recognizing β-glucans, polysaccharide components found in fungal cell walls, and certain bacteria. Upon ligand binding, CLEC7A activates intracellular signaling pathways through its immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-like motif, recruiting Syk kinase to trigger downstream responses such as phagocytosis, reactive oxygen species production, and cytokine release (e.g., TNF-α, IL-6). This receptor bridges microbial recognition to adaptive immunity by modulating T-cell responses.
CLEC7A antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, function, and signaling mechanisms. They are widely used in applications like flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, and Western blotting to investigate CLEC7A's role in antifungal defense, inflammatory diseases, and cancer. Dysregulation of CLEC7A has been linked to autoimmune disorders (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis), chronic inflammation, and tumor progression, making it a potential therapeutic target. Antibodies targeting CLEC7A also contribute to developing immunotherapies, such as antibody-drug conjugates or checkpoint inhibitors. Research continues to explore its dual role in host protection and pathological inflammation, emphasizing its importance in both infectious and non-infectious diseases.
×