
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
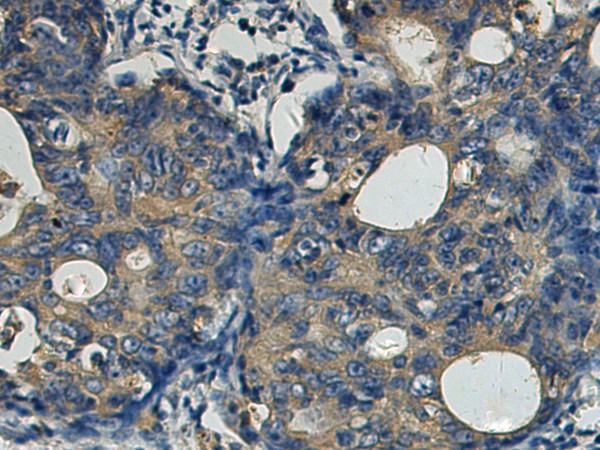
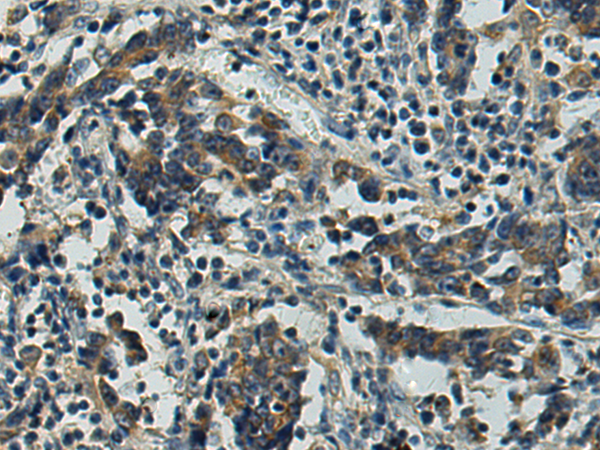
| IHC | 1/200-1/400 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CDC20A; p55CDC; bA276H19.3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CDC20 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CDC20抗体的3篇参考文献,信息基于公开研究整理(部分为示例性描述,实际引用时请核对原文):
---
1. **文献名称**: "CDC20 Antibody Characterization and Its Role in Mitotic Checkpoint Regulation"
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究验证了一种高特异性CDC20抗体的应用,证实CDC20在有丝分裂中通过APC/C复合体调控染色体分离,并探讨抗体在检测癌细胞异常CDC20表达中的诊断潜力。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Overexpression of CDC20 in Human Carcinomas: A Novel Biomarker Detected by Immunohistochemistry"
**作者**: Li X, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化分析多种癌症组织,利用CDC20抗体发现其在结直肠癌、乳腺癌中显著过表达,提示CDC20可能作为肿瘤预后标志物及治疗靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Development of a Monoclonal Antibody Against CDC20 for Functional Studies in Cell Cycle Progression"
**作者**: Chen R, et al.
**摘要**: 报道一种新型单克隆抗体的开发,该抗体能特异性识别CDC20蛋白,并通过抑制CDC20-APC/C相互作用延迟细胞周期进程,为研究有丝分裂调控机制提供工具。
---
如需具体文献DOI或补充更多研究,请提供更详细需求。
CDC20 (Cell Division Cycle 20) is a critical regulatory protein involved in cell cycle progression, specifically during the transition from metaphase to anaphase in mitosis. As a key coactivator of the Anaphase-Promoting Complex/Cyclosome (APC/C), CDC20 facilitates the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of mitotic regulators like securin and cyclin B, ensuring proper chromosome segregation and mitotic exit. Dysregulation of CDC20 is closely associated with genomic instability, aberrant cell proliferation, and tumorigenesis, making it a biomarker of interest in cancer research.
CDC20 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and functional interactions in cell cycle control. They are widely used in techniques such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and flow cytometry to quantify CDC20 levels in normal versus pathological tissues. Overexpression of CDC20 has been reported in various cancers, including breast, colorectal, and hepatocellular carcinomas, correlating with poor prognosis and therapeutic resistance. Researchers also employ these antibodies to investigate CDC20's role in checkpoint mechanisms, drug responses, and its potential as a therapeutic target.
Recent studies explore CDC20 inhibitors to disrupt cancer cell proliferation, highlighting its translational relevance. Commercial CDC20 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (human or murine) and validated for species reactivity and application compatibility.
×