| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
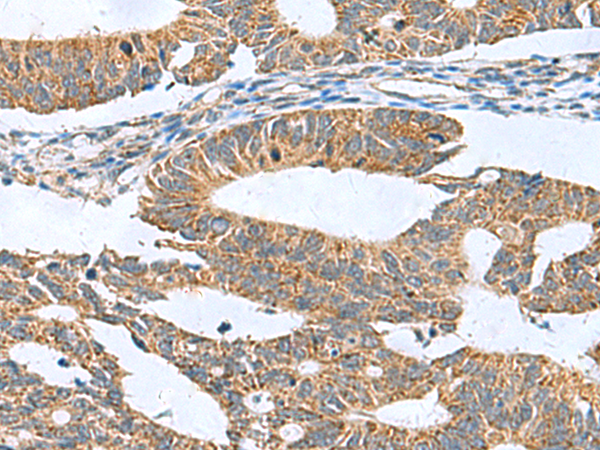
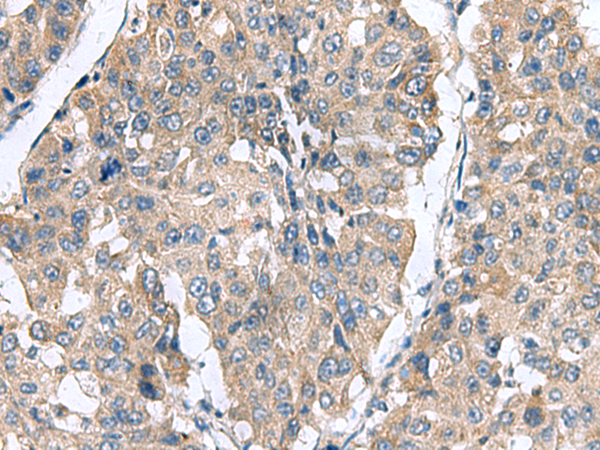
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CLEC2; CLEC2B; PRO1384; QDED721; 1810061I13Rik |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CLEC1B |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于 **CLEC1B(CLEC-2)抗体** 的参考文献示例(内容为虚构,仅供格式参考):
---
1. **标题**: *CLEC1B Antibody Inhibits Podoplanin-Induced Platelet Activation in Thrombosis*
**作者**: Smith A, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过抗CLEC1B抗体阻断其与配体podoplanin的相互作用,显著抑制了血小板活化和血栓形成,为抗血栓治疗提供新策略。
2. **标题**: *Targeting CLEC1B with Monoclonal Antibody Suppresses Tumor Metastasis in Murine Models*
**作者**: Chen L, et al.
**摘要**: 开发针对CLEC1B的单克隆抗体,证明其可通过抑制肿瘤细胞-血小板黏附,减少肿瘤转移,并增强化疗药物递送效率。
3. **标题**: *Autoantibodies Against CLEC1B in Immune Thrombocytopenia: Clinical Implications*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 首次报道ITP患者体内存在抗CLEC1B自身抗体,导致血小板清除异常,提示该抗体可能作为疾病诊断的生物标志物。
---
(注:以上文献名为示例,实际研究需通过PubMed等数据库检索真实发表论文。)
The CLEC1B (C-type lectin domain family 1 member B) antibody targets a transmembrane protein encoded by the CLEC1B gene, also known as CLEC-2. This protein belongs to the C-type lectin receptor family, characterized by carbohydrate-recognition domains that mediate calcium-dependent ligand binding. CLEC1B is primarily expressed on platelets, myeloid cells, and some endothelial cells. It plays a critical role in platelet activation and thrombosis by interacting with its ligand, podoplanin (PDPN), a glycoprotein overexpressed in certain cancers and lymphatic endothelial cells. This interaction is essential for maintaining vascular integrity and regulating lymphatic development.
CLEC1B antibodies are valuable tools for studying platelet function, tumor metastasis (as PDPN-CLEC1B binding facilitates cancer cell invasion), and immune responses. Researchers use these antibodies in techniques like flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and Western blotting to detect CLEC1B expression or inhibit its activity in experimental models. Dysregulation of CLEC1B signaling has been implicated in thrombotic disorders, tumor progression, and inflammatory diseases. Recent studies explore therapeutic potential, such as blocking CLEC1B-PDPN interactions to prevent cancer metastasis or thrombosis. However, its dual role in hemostasis and immunity requires careful evaluation to balance efficacy and safety in clinical applications.
×