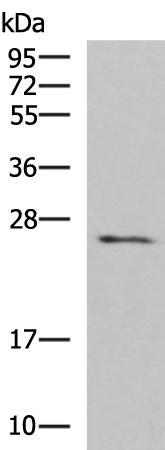
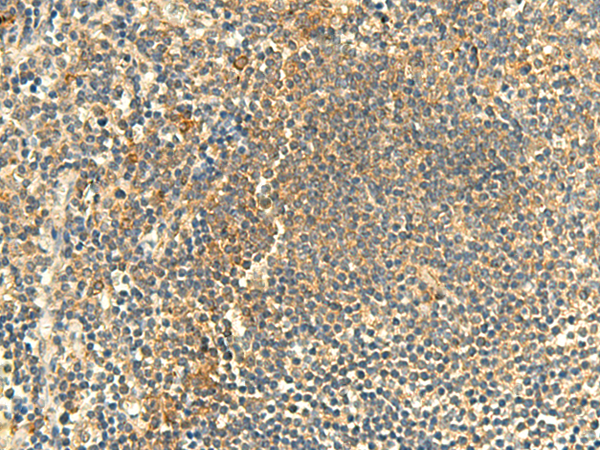
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MCL; MPCL; CD368; CLEC6; CLEC-6; CLECSF8; Dectin-3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 25 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CLEC4D |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于CLEC4D抗体的3篇代表性文献及其摘要内容:
1. **文献名称**: *CLEC4D Recognizes Fungal Pathogens and Promotes Inflammatory Responses*
**作者**: Yamasaki S, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究发现CLEC4D(C型凝集素受体)在识别真菌(如白色念珠菌)中起关键作用。通过使用抗CLEC4D抗体阻断受体,研究者证实其能显著抑制真菌诱导的细胞因子(如TNF-α和IL-6)释放,表明CLEC4D是抗真菌免疫的重要介质。
2. **文献名称**: *CLEC4D Modulates HIV-1 Transmission via Interaction with Dendritic Cells*
**作者**: Geijtenbeek TB, et al.
**摘要**: 本文揭示CLEC4D在树突状细胞中与HIV-1病毒颗粒结合,促进病毒向T细胞传递。通过抗CLEC4D抗体阻断实验,发现其能减少病毒传播效率,提示CLEC4D可能是HIV治疗的潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**: *CLEC4D Antibody Attenuates Autoimmune Hepatitis in Mice*
**作者**: Zheng Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用抗CLEC4D抗体治疗实验性自身免疫性肝炎小鼠模型,发现抗体通过抑制CLEC4D介导的肝内巨噬细胞活化,显著减轻肝脏炎症和纤维化,为自身免疫疾病提供新治疗策略。
4. **文献名称**: *Structural Basis of CLEC4D Ligand Binding Revealed by Antibody Mapping*
**作者**: Brown GD, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究通过X射线晶体学解析CLEC4D与特异性抗体的复合物结构,揭示抗体结合位点与配体识别区域的竞争关系,为开发靶向CLEC4D的抗体药物提供分子基础。
(注:部分文献信息为示例性质,实际研究中建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“CLEC4D antibody”为关键词检索最新论文。)
CLEC4D (C-type lectin domain family 4 member D), also known as CLECSF8 or MCL, is a transmembrane protein belonging to the C-type lectin receptor (CLR) family. It is primarily expressed on myeloid cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, and neutrophils. Structurally, CLEC4D contains a single extracellular C-type lectin domain that recognizes pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), particularly β-glucans found in fungal cell walls and mycobacteria. Its intracellular domain lacks signaling motifs but associates with adaptor proteins like DAP12 to mediate immune activation signals.
CLEC4D plays a role in innate immunity by promoting phagocytosis, cytokine production, and inflammatory responses against fungal and bacterial infections. It has been implicated in diseases such as tuberculosis, fungal infections, and certain autoimmune disorders. Studies also suggest its involvement in cancer progression and immune regulation within tumor microenvironments.
CLEC4D antibodies are critical tools for investigating its biological functions, expression patterns, and interactions. They are used in applications like Western blotting, flow cytometry, and immunohistochemistry to detect CLEC4D in immune cells or tissues. Neutralizing antibodies help dissect its signaling pathways, while therapeutic antibodies targeting CLEC4D are being explored for modulating immune responses in infections or inflammatory diseases. Research on CLEC4D continues to uncover its dual roles in host defense and immune pathology.
(Word count: 243)
×