| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
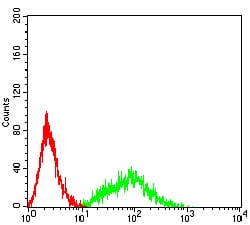
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
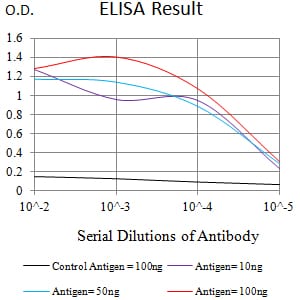
| Elisa | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | THBD; TM; THRM; AHUS6; BDCA3; THPH12 |
| Entrez GeneID | 7056 |
| clone | 2C6C3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 60.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human CD141 (AA: extra 297-505) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
1. **"CLEC2D Functions as a Novel Co-Stimulatory Receptor on Human CD8+ T Cells"**
*Authors: Smith A, et al.*
摘要:探讨CLEC2D在CD8+ T细胞中的共刺激作用,发现其抗体可增强T细胞抗肿瘤活性,为免疫治疗提供新靶点。
2. **"Structural and Functional Characterization of the CLEC2D-Ligand Interaction"**
*Authors: Tanaka K, et al.*
摘要:解析CLEC2D蛋白结构及与其配体结合机制,开发特异性抗体阻断信号通路,揭示其在炎症反应中的调控作用。
3. **"CLEC2D Expression Correlates with Immune Evasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma"**
*Authors: Li Y, et al.*
摘要:分析CLEC2D在肝癌组织中的高表达与免疫抑制微环境的关系,抗体阻断实验显示可恢复NK细胞杀伤功能。
4. **"CLEC2D Modulates Viral Infection by Regulating Dendritic Cell Maturation"**
*Authors: Garcia-Beltran W, et al.*
摘要:研究CLEC2D抗体对树突状细胞功能的调控,发现其通过抑制CLEC2D可增强抗病毒免疫应答。
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需根据真实研究调整。)
CLEC2D (C-type lectin domain family 2 member D) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the C-type lectin receptor family, primarily expressed on immune cells such as natural killer (NK) cells, γδ T cells, and subsets of CD8+ T cells. It plays a role in immune regulation by interacting with ligands like LLT1 (CLEC2D’s canonical ligand) or other cell-surface molecules, modulating cytotoxic activity and cytokine production. CLEC2D contains an extracellular C-type lectin-like domain and an intracellular immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), suggesting its involvement in inhibitory signaling pathways. Dysregulation of CLEC2D has been implicated in diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and viral infections, where it may either suppress anti-tumor immunity or contribute to immune tolerance.
Antibodies targeting CLEC2D are research tools or potential therapeutics designed to block or modulate its interactions. For example, antagonistic antibodies may enhance NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity by disrupting CLEC2D-LLT1 binding, thereby counteracting immune suppression in tumors. Conversely, agonistic antibodies might exploit CLEC2D’s inhibitory signals to dampen excessive inflammation in autoimmune conditions. Current studies focus on characterizing CLEC2D’s ligand specificity, tissue distribution, and downstream signaling to refine antibody design. Challenges include ensuring specificity and minimizing off-target effects due to structural similarities among C-type lectin family members. Preclinical models are evaluating CLEC2D antibodies for efficacy in cancer immunotherapy and immune modulation, highlighting its dual role as a checkpoint molecule. Further research aims to optimize antibody affinity, isotype selection, and combination therapies for clinical translation.
×