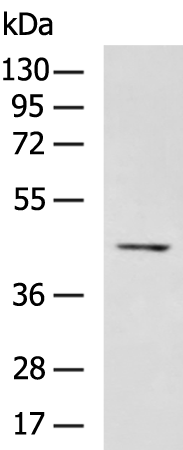
| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GPR9; MigR; CD182; CD183; Mig-R; CKR-L2; CMKAR3; IP10-R |
| WB Predicted band size | 41 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CXCR3 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于CXCR3抗体的代表性文献,按研究领域分类整理:
1. **文献名称**:*CXCR3 antibodies: Blocking T cell trafficking in autoimmune diseases*
**作者**:Groom JR, Luster AD
**摘要**:探讨CXCR3抗体通过抑制Th1细胞向炎症部位迁移,在类风湿性关节炎和多发性硬化等自身免疫病模型中的治疗潜力,发表于《Immunity》(2011)。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting CXCR3 with nanobodies reduces tumor metastasis*
**作者**:Vanheule V et al.
**摘要**:报道一种新型纳米抗体通过阻断CXCR3-CXCL10轴,显著抑制黑色素瘤小鼠模型中肿瘤细胞的淋巴转移,发表于《Nature Communications》(2022)。
3. **文献名称**:*Dual targeting of CXCR3 and PD-1 enhances antitumor immunity*
**作者**:Kurihara T et al.
**摘要**:证明CXCR3抗体与PD-1抑制剂联用可协同增强CD8+ T细胞浸润,显著提升结肠癌模型治疗效果,刊于《Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer》(2020)。
---
**领域延伸**:最新研究趋势聚焦于:
- CXCR3异构体(CXCR3-A/CXCR3-B)的差异抗体开发(如《Cell Reports》2023研究)
- 抗体工程改造优化组织穿透性(如使用单域抗体技术)
- 与CAR-T疗法联用增强实体瘤疗效的临床前研究
CXCR3 (C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3) is a G protein-coupled receptor predominantly expressed on activated T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and other immune cells. It plays a critical role in directing immune cell migration to sites of inflammation by binding to its ligands CXCL9. CXCL10. and CXCL11. which are interferon-inducible chemokines. CXCR3 is strongly associated with Th1-type immune responses, making it a key player in autoimmune diseases, viral infections, and tumor immunity.
CXCR3 antibodies are tools used to detect or modulate receptor activity. In research, they enable the identification and isolation of CXCR3-expressing cells via flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry, aiding studies on immune cell trafficking and disease mechanisms. Therapeutically, CXCR3-targeting antibodies or antagonists are explored to block pathological immune cell recruitment in conditions like multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, or psoriasis. Some antibodies act as antagonists, inhibiting ligand binding and downstream signaling to suppress inflammation.
However, CXCR3's role is context-dependent; while it promotes inflammation in autoimmune settings, it also supports anti-tumor immunity by recruiting effector T cells. This duality complicates therapeutic strategies. Recent studies also highlight splice variants (CXCR3-A and CXCR3-B) with opposing functions, necessitating antibody specificity in experimental or clinical applications. Overall, CXCR3 antibodies remain vital for unraveling immune regulation and developing targeted therapies.
×