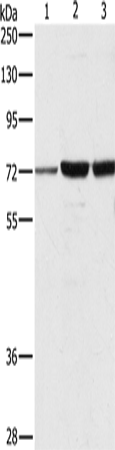
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | P62DOK |
| WB Predicted band size | 52 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human DOK1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于DOK1抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*DOK1 inhibits T cell activation and promotes immunological tolerance*
**作者**:Yamanashi Y, et al.
**摘要**:本研究通过Western blot和免疫共沉淀技术,利用DOK1特异性抗体证实了DOK1蛋白在T细胞受体(TCR)信号通路中的抑制作用。结果表明,DOK1通过招募磷酸酶抑制下游激酶活性,调控T细胞活化和自身免疫耐受。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Downregulation of DOK1 in chronic myeloid leukemia correlates with disease progression*
**作者**:Jiang H, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫印迹和免疫组化分析慢性髓系白血病(CML)样本,发现DOK1蛋白表达随疾病进展显著降低。研究使用DOK1抗体证实其作为肿瘤抑制因子的功能,并揭示其缺失可能导致BCR-ABL信号通路异常激活。
---
3. **文献名称**:*DOK1 modulates insulin signaling by binding to IRS-1 in hepatocytes*
**作者**:Wick MJ, et al.
**摘要**:利用DOK1抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,发现肝细胞中DOK1与胰岛素受体底物(IRS-1)相互作用,负向调控胰岛素信号通路。研究揭示了DOK1在代谢性疾病(如糖尿病)中的潜在作用机制。
---
这些文献均通过DOK1抗体进行蛋白功能验证,涵盖免疫调节、肿瘤发生及代谢调控等领域。如需具体期刊信息或发表年份,可进一步补充。
The DOK1 (Docking Protein 1) antibody is a tool used to study the DOK1 protein, a key adaptor molecule involved in signal transduction pathways. DOK1. part of the DOK family (DOK1–7), is characterized by an N-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain, a central phosphotyrosine-binding (PTB) domain, and a C-terminal region with multiple tyrosine phosphorylation sites. It acts downstream of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and cytokine receptors, mediating interactions with signaling molecules like SHP2. RasGAP, and CSK to regulate cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis.
DOK1 is widely expressed in hematopoietic cells and functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively modulating oncogenic signaling. Studies link reduced DOK1 expression to chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), inflammatory disorders, and autoimmune diseases, often due to promoter hypermethylation. Its role in immune regulation includes inhibiting T-cell activation and dampening B-cell receptor signaling, highlighting its importance in maintaining immune homeostasis.
DOK1 antibodies are essential for detecting DOK1 expression, phosphorylation status, and interactions in techniques like Western blotting, immunoprecipitation, and immunohistochemistry. Research using these antibodies has advanced understanding of DOK1’s dual roles in cancer suppression and immune modulation, offering insights into therapeutic strategies targeting DOK1-related pathways in malignancies and immune dysregulation.
×