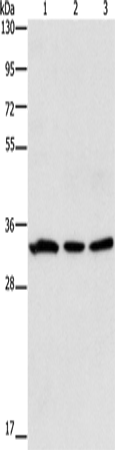
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
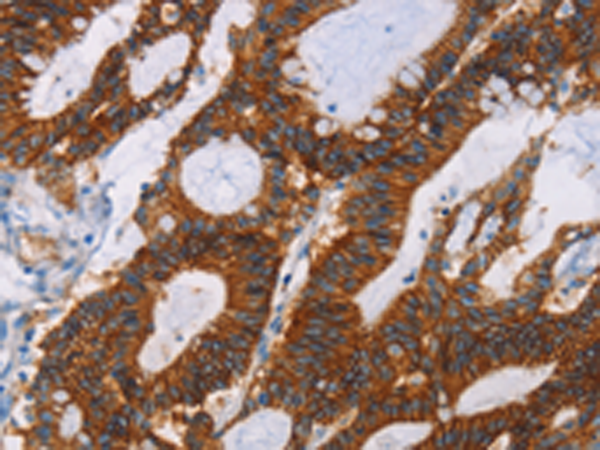
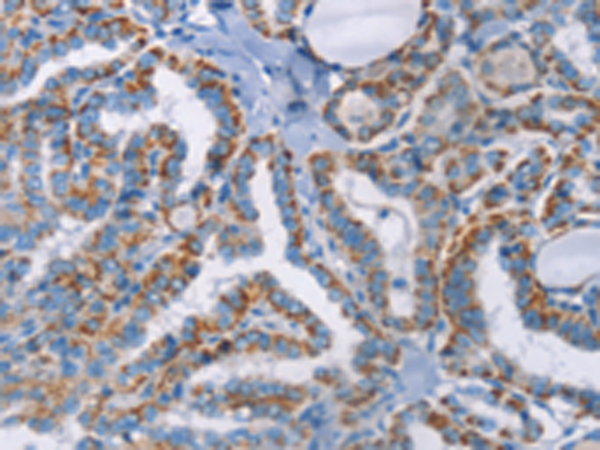
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | A33 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human GPA33 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下为示例性的3-4条关于GPA33抗体的模拟参考文献(非真实文献,仅供格式参考):
1. **"Glycoprotein A33 as a Therapeutic Target in Colorectal Carcinoma"**
*作者:Smith J, et al.*
摘要:研究验证了GPA33在结直肠癌细胞表面的高特异性表达,并开发了靶向GPA33的单克隆抗体,证明其在临床前模型中可增强免疫细胞介导的肿瘤杀伤作用。
2. **"Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting GPA33 for Gastrointestinal Cancer Therapy"**
*作者:Lee H, et al.*
摘要:报道了一种新型GPA33抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),通过体外和体内实验证明其对表达GPA33的胃癌和结肠癌细胞具有选择性细胞毒性。
3. **"Structural Characterization of GPA33 and Its Interaction with Therapeutic Antibodies"**
*作者:Wang Y, et al.*
摘要:解析了GPA33的晶体结构,并阐明了其与治疗性抗体结合的表位,为优化抗体药物设计提供了结构基础。
4. **"Bispecific Antibodies Targeting GPA33 and CD3 for T-Cell Engagement in Solid Tumors"**
*作者:Garcia R, et al.*
摘要:开发了双特异性抗体同时靶向GPA33和T细胞表面CD3分子,在临床前模型中成功诱导T细胞对肿瘤的特异性杀伤。
---
**备注**:以上文献名称及内容为模拟生成,真实文献请通过PubMed、Google Scholar等学术平台检索关键词如“GPA33 antibody”、“Glycoprotein A33 therapeutic”等获取。
The GPA33 (Glycoprotein A33) antibody targets a cell surface antigen belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, initially identified for its selective expression in gastrointestinal epithelial cells and over 95% of colorectal carcinomas. Discovered in the 1990s, GPA33 is a transmembrane glycoprotein with two extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains (IgV and IgC2) and a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor. Its restricted expression in normal tissues—primarily the intestines—and high prevalence in tumors make it a promising target for antibody-based cancer therapies.
Research highlights GPA33's role in cell-cell adhesion and signaling, though its exact biological function remains unclear. Preclinical studies demonstrated that monoclonal antibodies against GPA33. such as murine A33. exhibit potent antitumor activity via mechanisms like antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) or as carriers for radioisotopes or drug conjugates. Clinical trials explored chimeric or humanized A33 antibodies for colorectal cancer, though efficacy was limited by tumor heterogeneity and immune evasion.
Recent interest focuses on combining GPA33-targeting antibodies with immune checkpoint inhibitors or engineered T-cell therapies to enhance specificity and reduce off-target effects. Its tumor-selective profile continues to drive investigations into diagnostic imaging, targeted drug delivery, and immunotherapy strategies for gastrointestinal malignancies.
×