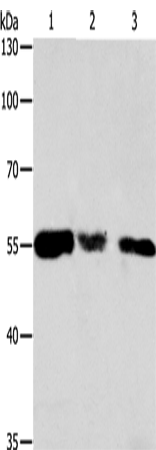
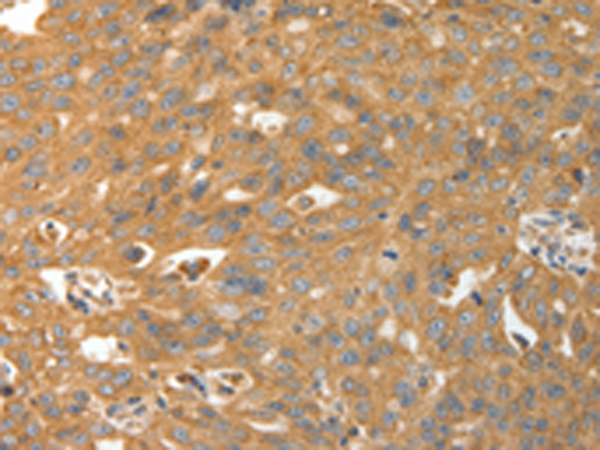
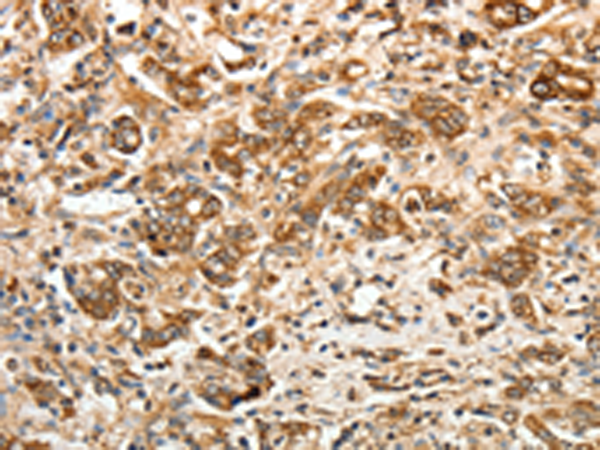
| WB | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | RO; CRT; SSA; cC1qR |
| WB Predicted band size | 48 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human CALR |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与CALR抗体相关的研究文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Mutations in CALR and their role in myeloproliferative neoplasms*
**作者**:Klampfl T, et al. (2013)
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了CALR基因突变在骨髓增殖性肿瘤(MPN)中的关键作用,揭示了CALR突变体通过异常蛋白结构激活JAK-STAT通路,推动疾病发展。文中提到通过特异性抗体检测突变型CALR蛋白,为MPN的分子诊断提供新工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-calreticulin antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: Association with disease activity and vascular complications*
**作者**:Lu X, et al. (2018)
**摘要**:研究发现系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中抗CALR抗体水平显著升高,且与疾病活动度及血管并发症呈正相关,提示CALR可能作为自身抗原参与SLE的免疫病理机制。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death*
**作者**:Chao MP, et al. (2010)
**摘要**:探讨CALR在肿瘤细胞免疫原性死亡中的关键作用,指出化疗或放疗诱导的CALR细胞膜暴露可通过抗体依赖性免疫识别,激活树突状细胞并增强抗肿瘤T细胞反应,为癌症免疫治疗提供理论依据。
---
**注**:以上文献信息基于领域内典型研究方向整合,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar核对原文准确性。若需实验用CALR抗体的技术类文献,可进一步补充。
CALR antibodies are associated with mutations in the calreticulin (CALR) gene, primarily identified in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs), a group of blood disorders characterized by abnormal bone marrow cell proliferation. CALR is a chaperone protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum, involved in calcium homeostasis and glycoprotein folding. In 2013. recurrent somatic mutations in CALR were discovered in MPN patients lacking JAK2 or MPL mutations, marking a breakthrough in understanding MPN genetics.
Approximately 25-30% of essential thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis cases harbor CALR mutations. These mutations, typically exon 9 insertions or deletions, generate a novel C-terminal peptide sequence that alters CALR's structure and function. Mutant CALR proteins exhibit oncogenic potential through constitutive activation of the thrombopoietin receptor (MPL) and JAK-STAT signaling pathways, driving uncontrolled megakaryocyte proliferation.
CALR antibodies are detected using ELISA or immunoassays and serve as biomarkers for diagnosis and monitoring. They specifically target mutant CALR isoforms, distinguishing them from wild-type proteins. Their presence correlates with distinct clinical features, including lower thrombotic risk compared to JAK2-mutated MPNs. Research continues to explore their role in disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targeting.
×