
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
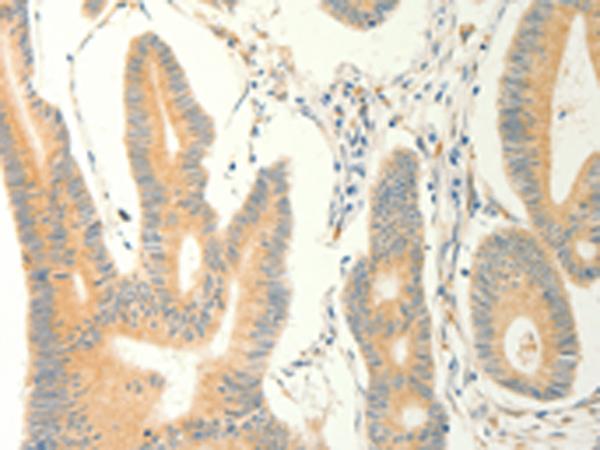
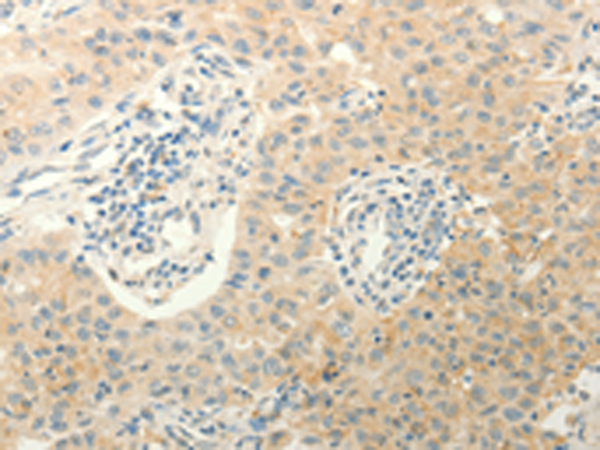
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | p55; erg-3 |
| WB Predicted band size | 54 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ERG |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ERG抗体的3篇参考文献示例,涵盖不同应用领域:
---
### 1. **"Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer"**
**作者**: Tomlins, S. A. 等 (2005. *Science*)
**摘要**: 该研究首次揭示了前列腺癌中TMPRSS2与ERG等ETS家族基因的融合现象,证实ERG过表达与肿瘤发生相关,为ERG抗体作为前列腺癌特异性诊断标记奠定基础。
---
### 2. **"ERG transcription factor as an immunohistochemical marker for vascular endothelial tumors and prostate carcinoma"**
**作者**: Folpe, A. L. 等 (2011. *Modern Pathology*)
**摘要**: 研究评估ERG抗体在血管源性肿瘤(如血管肉瘤)和前列腺癌中的表达,显示ERG对血管内皮细胞的高特异性,建议将其作为联合诊断标记以提高准确性。
---
### 3. **"ERG expression in epithelioid sarcoma: a diagnostic pitfall"**
**作者**: McCluggage, W. G. 等 (2013. *Histopathology*)
**摘要**: 探讨ERG抗体在子宫腺肉瘤等上皮样肿瘤中的表达,提示需结合其他标记物避免误诊,强调其在特定肉瘤中的诊断价值及局限性。
---
### 4. **"ERG protein expression in diagnostic prostate pathology: correlation with TMPRSS2-ERG gene rearrangement"**
**作者**: Park, K. 等 (2012. *The American Journal of Surgical Pathology*)
**摘要**: 分析ERG抗体表达与TMPRSS2-ERG基因融合的相关性,证明其作为前列腺癌分子分型的可靠替代指标,并与侵袭性病理特征相关。
---
**注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或学术数据库核对详细信息。
ERG (ETS-related gene) antibodies are immunohistochemical markers targeting the ERG protein, a member of the ETS transcription factor family. The ERG gene plays critical roles in endothelial development, angiogenesis, and cell differentiation. It is highly expressed in normal endothelial cells, hematopoietic stem cells, and specific tissues like the prostate. Pathologically, ERG overexpression is strongly associated with malignancies, particularly prostate adenocarcinoma, where the TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion (present in ~50% of cases) drives oncogenic ERG expression. This fusion serves as a hallmark molecular alteration, making ERG antibodies valuable diagnostic tools for confirming prostatic origin in metastatic or poorly differentiated tumors.
ERG antibodies also aid in identifying vascular neoplasms (e.g., epithelioid hemangioendothelioma) and mesenchymal tumors with EWSR1-ERG fusions. Their specificity for endothelial differentiation helps distinguish vascular lesions from mimics. However, ERG expression isn’t entirely tumor-specific; normal endothelial cells and non-prostatic tumors (e.g., Ewing sarcoma) may also exhibit positivity. Interpretation thus requires correlation with clinical, morphological, and additional biomarkers. Commercially available monoclonal ERG antibodies (e.g., clone EPR3864) demonstrate high sensitivity and nuclear-specific staining, optimizing utility in diagnostic pathology. Overall, ERG antibodies are indispensable for tumor classification, molecular-subtype stratification, and research into ERG-driven oncogenic pathways.
×