
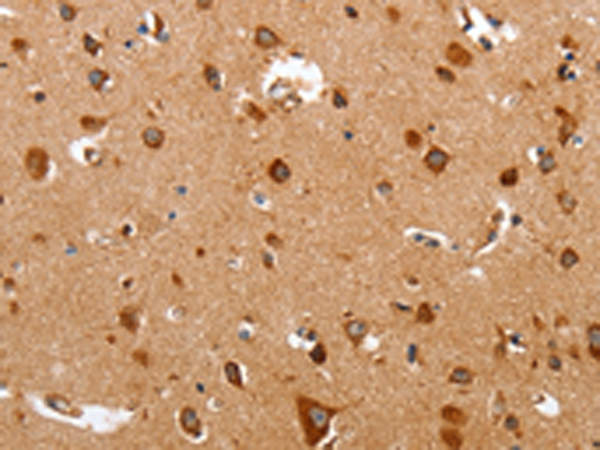
| WB | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
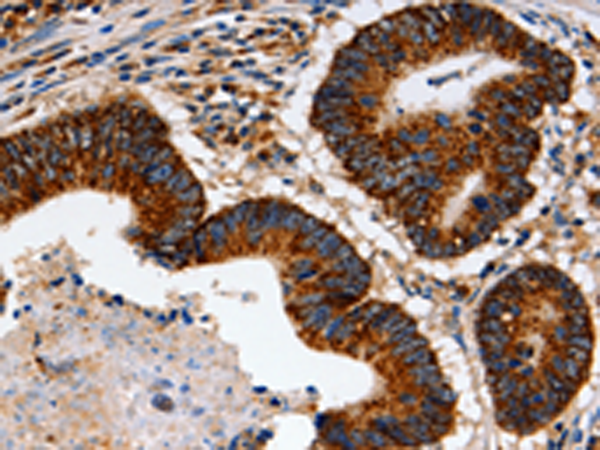
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | HSP75, HSP90L |
| WB Predicted band size | 80 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TRAP1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TRAP1抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*TRAP1 regulates apoptosis in colorectal cancer via the ERK signaling pathway*
**作者**:Amoroso MR 等
**摘要**:研究利用TRAP1特异性抗体分析其在结直肠癌组织中的表达,发现TRAP1高表达与化疗耐药性和患者预后不良相关,机制涉及ERK信号通路调控凋亡抵抗。
2. **文献名称**:*Mitochondrial TRAP1 inhibits oxidative stress and cellular senescence*
**作者**:Yoshida S 等
**摘要**:通过免疫印迹(TRAP1抗体)和免疫荧光技术,证实TRAP1在线粒体中通过抑制活性氧(ROS)积累延缓细胞衰老,为抗氧化治疗提供潜在靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting TRAP1 as a therapeutic strategy in prostate cancer*
**作者**:Costa AC 等
**摘要**:研究开发了靶向TRAP1的小分子抑制剂,并利用TRAP1抗体验证其下调效果,显示抑制TRAP1可增强前列腺癌细胞对凋亡的敏感性,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
4. **文献名称**:*TRAP1 interacts with autophagy-related proteins in Parkinson's disease models*
**作者**:Butler EK 等
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(TRAP1抗体)发现TRAP1与自噬蛋白(如LC3)相互作用,调控神经细胞线粒体稳态,为神经退行性疾病机制提供新见解。
注:以上内容基于领域内典型研究方向概括,实际文献需通过数据库(如PubMed)检索确认具体细节。
TRAP1 (Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein 1), also known as HSP75. is a mitochondrial chaperone belonging to the heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) family. It plays a critical role in regulating cellular stress responses, oxidative phosphorylation, apoptosis, and metabolic reprogramming. TRAP1 is structurally distinct from cytosolic HSP90 due to its N-terminal mitochondrial targeting sequence and unique ATP-binding domain. Studies have linked TRAP1 to cancer progression, as it promotes tumor cell survival under hypoxic or drug-treated conditions by inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening and cytochrome c release.
TRAP1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both physiological and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate TRAP1's role in diseases, particularly cancers. Commercial TRAP1 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes, such as the N-terminal or ATPase domains, with validation across species including human, mouse, and rat. Researchers have observed TRAP1 overexpression in various cancers, including colorectal, prostate, and ovarian cancers, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker. However, antibody specificity remains a challenge, requiring careful validation using knockout controls or siRNA-mediated silencing. Recent interest in TRAP1 inhibitors for anticancer therapy has further driven the demand for reliable antibodies to assess target engagement and treatment efficacy.
×