| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
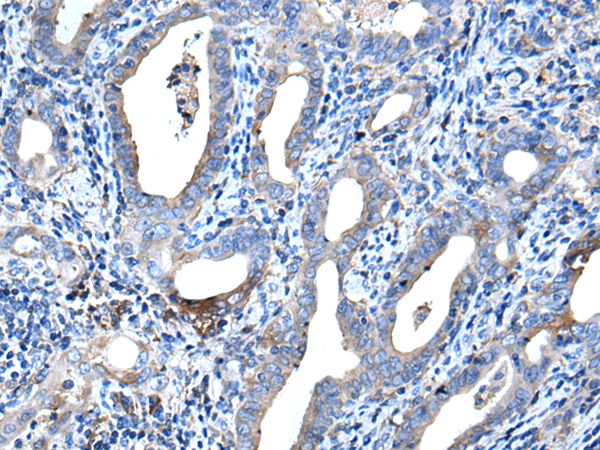
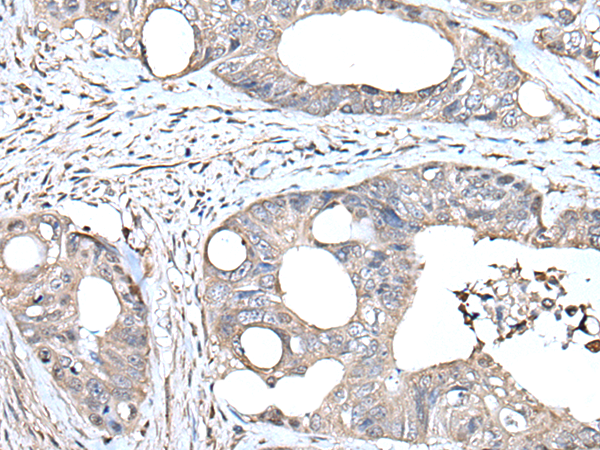
| IHC | 1/25-1/100 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | IL-2; TCGF; lymphokine |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Full length fusion protein |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇与IL-2抗体相关的代表性文献概览:
1. **"Structural basis of the IL-2/IL-2 receptor alpha chain interaction"**
*作者:K.D. Smith et al. (2003)*
摘要:通过X射线晶体学解析IL-2与其受体α链(IL-2Rα/CD25)的结合结构,揭示了抗体靶向IL-2/IL-2Rα互作界面的分子机制,为开发阻断性抗体提供结构基础。
2. **"Selective targeting of engineered IL-2 therapy to regulatory T cells enhances antitumor immunity"**
*作者:T.R. Malek et al. (2018)*
摘要:研究团队设计了一种工程化IL-2抗体融合蛋白(IL-2/CD25复合物),选择性激活调节性T细胞(Tregs),在肿瘤模型中验证了其增强抗肿瘤免疫反应的潜力。
3. **"Anti-IL-2 monoclonal antibody enhances autoimmune pathology by disrupting IL-2 signaling"**
*作者:C.M. Hogquist et al. (2005)*
摘要:报道了一种阻断IL-2信号的单克隆抗体(JES6-1A12),发现其在小鼠模型中通过抑制IL-2介导的T细胞稳态,加剧了自身免疫性疾病进展,提示IL-2抗体的双向调节作用。
4. **"IL-2 antibody drug conjugates for targeted cancer immunotherapy"**
*作者:R.D. Schreiber et al. (2021)*
摘要:开发新型IL-2抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),通过抗体靶向肿瘤微环境递送IL-2激动剂,在临床前模型中显著增强抗肿瘤活性并降低全身毒性。
(注:以上文献信息为示例性简化内容,实际引用需核对原始文献)
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a cytokine critical for immune regulation, primarily produced by activated T cells. It promotes the proliferation and differentiation of T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and regulatory T cells (Tregs), balancing immune activation and tolerance. IL-2 exerts its effects by binding to heterotrimeric receptors composed of α (CD25), β (CD122), and γ (CD132) chains. The high-affinity receptor (αβγ) is expressed on Tregs and activated T cells, while intermediate-affinity receptors (βγ) are found on NK cells and memory T cells.
IL-2-targeting antibodies have emerged as therapeutic tools to modulate immune responses. Agonistic antibodies, such as those targeting the βγ receptor subunits, aim to boost anti-tumor immunity by selectively activating effector T cells and NK cells, bypassing Treg stimulation. Conversely, antagonistic antibodies, like those blocking CD25. inhibit IL-2 signaling to suppress overactive immune responses in autoimmune diseases or transplant rejection.
Clinical development has faced challenges, including toxicity from systemic immune activation and the pleiotropic nature of IL-2 signaling. To address this, engineered IL-2 variants and antibody-cytokine fusion proteins (e.g., immunocytokines) have been designed to improve specificity, prolong half-life, or reduce off-target effects. For example, "not-alpha" IL-2 analogs preferentially bind βγ receptors, enhancing anti-cancer activity while minimizing Treg expansion.
IL-2 antibodies continue to be explored in cancer immunotherapy, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases, reflecting their dual role in amplifying or dampening immunity based on therapeutic context.
×