
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
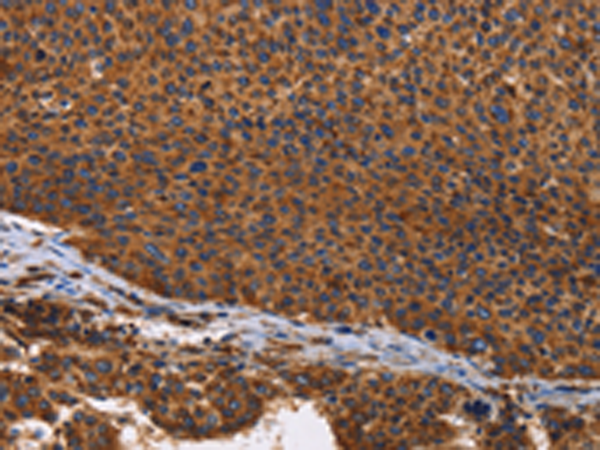
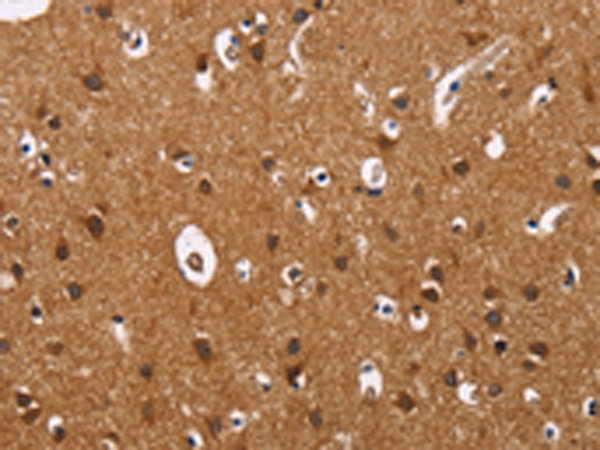
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | P59; ILK-1; ILK-2; p59ILK |
| WB Predicted band size | 51 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human ILK |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于ILK(整合素连接激酶)抗体的3篇代表性文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Integrin-linked kinase (ILK): a regulator of integrin and growth-factor signalling*
**作者**:Hannigan, G.E., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次报道了ILK在整合素介导的细胞-基质相互作用中的关键作用,利用特异性抗体证实了ILK通过与整合素β1亚基结合调控细胞黏附和存活,并影响下游信号通路(如Akt/PKB)。
---
2. **文献名称**:*ILK: a pseudokinase in the center of actin-cytoskeleton reorganization*
**作者**:Legate, K.R., et al.
**摘要**:文章综述了ILK在细胞骨架重塑和力学信号传导中的功能,通过抗体阻断实验表明ILK与PARVB(parvin)等蛋白互作,协调肌动蛋白动态变化,影响胚胎发育和组织稳态。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Inhibition of integrin-linked kinase suppresses angiogenesis and induces tumor cell apoptosis*
**作者**:Persad, S., et al.
**摘要**:研究利用ILK特异性抗体和小分子抑制剂,证明抑制ILK活性可阻断VEGF介导的血管生成,并通过下调NF-κB通路促进肿瘤细胞凋亡,提示ILK作为癌症治疗靶点的潜力。
---
如需具体实验中使用ILK抗体的技术细节,可进一步检索方法学文献(如*Journal of Biological Chemistry*或*Cell Signaling*相关文章)。
Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is a ubiquitously expressed intracellular serine/threonine protein kinase that plays a pivotal role in connecting the extracellular matrix (ECM) to intracellular signaling networks. It was first identified in the mid-1990s as a binding partner for the cytoplasmic domain of β1-integrin, a critical cell adhesion receptor. Structurally, ILK consists of four ankyrin repeats at the N-terminus, a pleckstrin homology (PH)-like domain, and a kinase-like domain at the C-terminus. Although its catalytic activity has been debated, ILK is recognized as a key regulatory node in focal adhesions, coordinating signals from integrins, growth factors, and mechanical stimuli to regulate cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and survival.
ILK antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to assess ILK levels in tissues or cultured cells. High-quality ILK antibodies exhibit specificity for distinct isoforms or phosphorylation states, enabling precise investigation of ILK’s role in pathways such as Akt/PKB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Dysregulation of ILK is implicated in cancer progression, fibrosis, and cardiovascular diseases, making these antibodies valuable for mechanistic studies and therapeutic targeting. However, challenges remain in ensuring antibody specificity due to ILK’s structural homology with other kinases. Validation using knockout controls or functional assays is critical to avoid off-target artifacts. Overall, ILK antibodies continue to advance our understanding of cell-ECM interactions and their implications in disease.
×