
| WB | 1/200-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
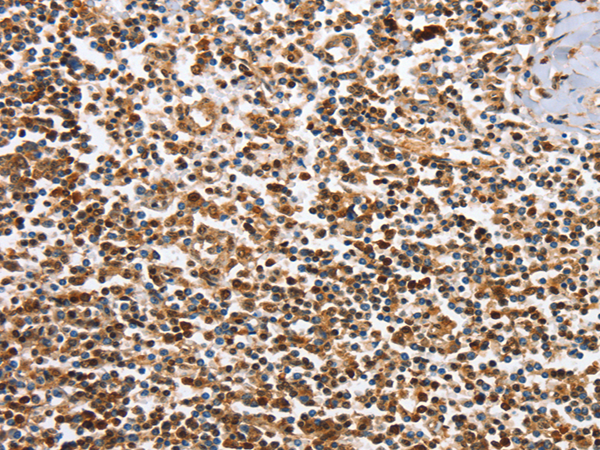
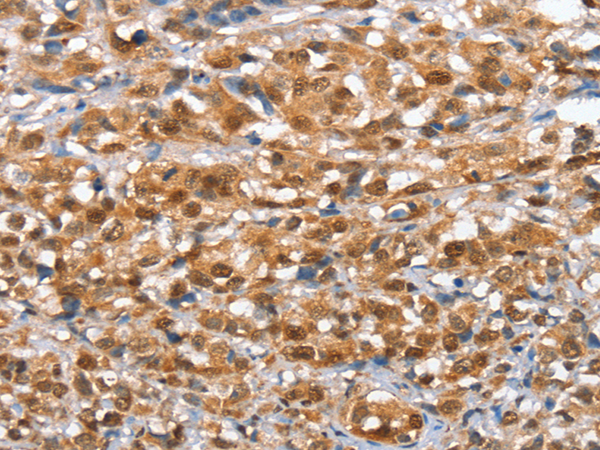
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ASRT5; IRAKM |
| WB Predicted band size | 68 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human IRAK3 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于IRAK3抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及简要摘要内容:
---
1. **"IRAK3 regulates inflammation and immune responses by modulating TLR signaling"**
*作者:Li X, Qin J, etc.*
摘要:该研究利用IRAK3特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫沉淀技术,揭示IRAK3通过负调控TLR/MyD88通路抑制NF-κB激活,从而抑制炎症因子释放,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新靶点。
2. **"IRAK3 deficiency promotes oncogenic Kras-driven lung cancer through deregulation of IL-6/STAT3 signaling"**
*作者:Wang Y, Chen Z, etc.*
摘要:通过IRAK3抗体进行组织染色和蛋白质分析,发现IRAK3缺失导致STAT3信号异常激活,促进肺癌进展,表明IRAK3在肿瘤微环境中的免疫调节作用。
3. **"A novel IRAK3 antibody reveals its role in metabolic reprogramming of macrophages"**
*作者:Smith A, Johnson R, etc.*
摘要:研究开发了一种高特异性IRAK3抗体,证实IRAK3通过调控线粒体代谢影响巨噬细胞极化,为代谢性疾病中IRAK3的功能机制提供了实验依据。
---
以上文献均聚焦于IRAK3在免疫信号通路或疾病中的功能研究,并明确提及使用IRAK3抗体作为关键实验工具。如需具体期刊信息或发表年份,可进一步补充关键词检索。
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 3 (IRAK3), also known as IRAK-M, is a critical regulator of innate immune signaling pathways. As a member of the IRAK family, it functions as a negative feedback inhibitor of Toll-like receptor (TLR) and interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) signaling. Unlike other IRAK kinases (e.g., IRAK1. IRAK4), IRAK3 lacks kinase activity due to substitutions in key catalytic residues. Instead, it modulates immune responses by preventing the dissociation of IRAK1 and IRAK4 from receptor complexes, thereby inhibiting downstream NF-κB and MAPK activation. This regulatory role limits excessive inflammation, maintaining immune homeostasis.
IRAK3 is predominantly expressed in monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Its expression is induced by inflammatory stimuli, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), highlighting its involvement in dampening prolonged immune activation. Dysregulation of IRAK3 has been implicated in chronic inflammatory diseases, sepsis, cancer, and autoimmune disorders. For example, reduced IRAK3 levels correlate with hyperinflammatory responses, while its overexpression may contribute to immunosuppression in tumors.
Antibodies targeting IRAK3 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in immune cells. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. Such research aids in elucidating IRAK3’s role in disease mechanisms and its potential as a therapeutic target or biomarker for immune-related conditions.
×