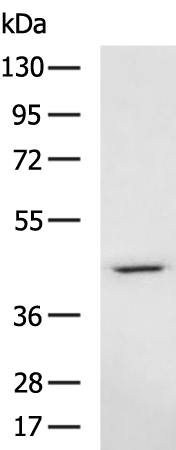
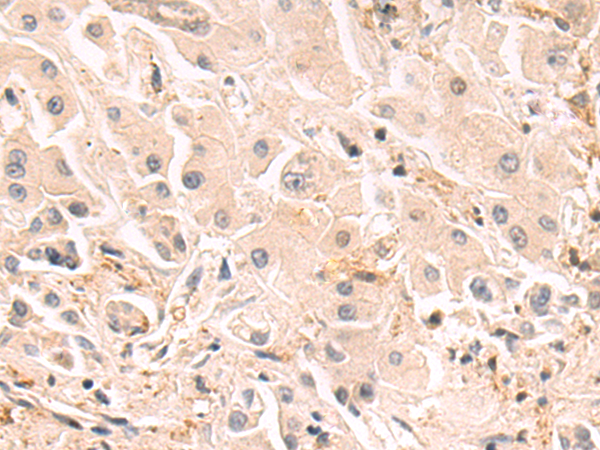
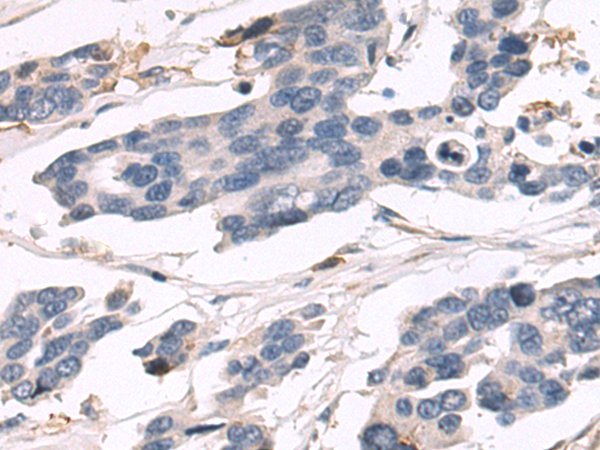
| WB | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CD305; LAIR-1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 31 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human LAIR1 |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于LAIR1抗体的3篇文献摘要信息(文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括):
---
1. **文献名称**:*LAIR-1 agonism as a therapy for acute myeloid leukemia*
**作者**:Matteo F. et al. (2022)
**摘要内容**:本研究探讨了LAIR1激动型抗体在急性髓系白血病(AML)中的治疗潜力。通过体外实验和小鼠模型,发现激活LAIR1信号可抑制AML细胞增殖并诱导凋亡,表明其可能成为免疫检查点治疗的新靶点。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of LAIR1 targeting by monoclonal antibodies for collagen binding inhibition*
**作者**:Li Y. et al. (2020)
**摘要内容**:研究解析了LAIR1与不同单克隆抗体的复合物晶体结构,揭示了抗体阻断LAIR1与胶原结合的分子机制,为设计靶向LAIR1的免疫调节药物提供了结构基础。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Bispecific antibody targeting LAIR1 and PD-1 enhances anti-tumor immunity*
**作者**:Wang X. et al. (2021)
**摘要内容**:开发了一种同时靶向LAIR1和PD-1的双特异性抗体,证明其可协同增强T细胞活性,在黑色素瘤模型中显著抑制肿瘤生长,提示联合免疫检查点阻断策略的有效性。
---
4. **文献名称**:*LAIR1 antibody-mediated suppression of autoimmune inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis models*
**作者**:Kumar S. et al. (2019)
**摘要内容**:研究发现抗LAIR1抗体通过抑制单核细胞和巨噬细胞的促炎因子分泌,减轻类风湿性关节炎小鼠模型的关节炎症,为自身免疫疾病治疗提供新思路。
---
注:以上文献信息为示例性质,具体内容请以实际发表文献为准。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词“LAIR1 antibody”获取最新研究。
The leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor 1 (LAIR1), also known as CD305. is an inhibitory immune checkpoint receptor belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Expressed broadly on immune cells, including T cells, B cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells, LAIR1 contains immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs) that recruit phosphatases to dampen cellular activation signals. It binds collagen and collagen-like molecules, serving as a sensor for extracellular matrix (ECM) components. This interaction plays a role in maintaining immune homeostasis by suppressing excessive immune responses, particularly in contexts of tissue remodeling or damage.
LAIR1’s immunosuppressive function has dual implications in disease. In cancer, tumor-derived collagen or LAIR1 ligands in the microenvironment may engage LAIR1 to evade immune surveillance, promoting tolerance. Conversely, in autoimmune disorders, excessive LAIR1 signaling might contribute to immune suppression, limiting pathogenic responses. LAIR1-targeting antibodies are being explored therapeutically: blocking antibodies aim to disrupt inhibitory signaling in cancers, potentially enhancing antitumor immunity, while agonist antibodies could suppress hyperactive immune cells in autoimmunity.
Recent studies also highlight LAIR1’s role in regulating memory T cells and its crosstalk with other checkpoints like PD-1. Preclinical models demonstrate that LAIR1 blockade synergizes with existing immunotherapies, underscoring its potential as a novel target. However, balancing therapeutic efficacy with autoimmune risks remains a critical challenge in development.
×