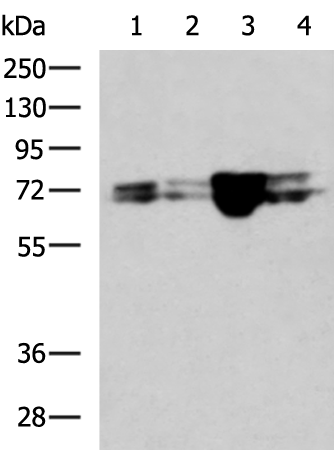
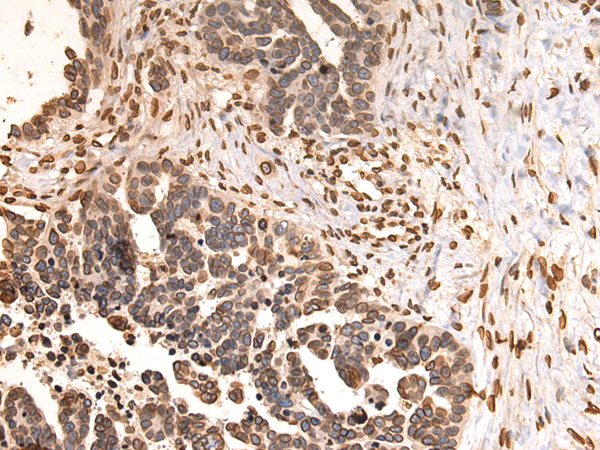
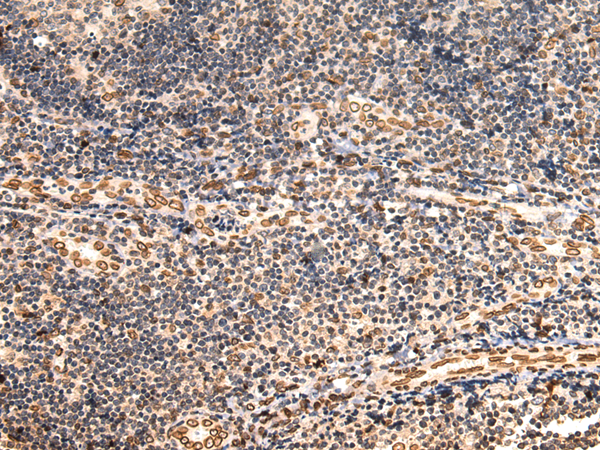
| WB | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | FPL; IDC; LFP; CDDC; EMD2; FPLD; HGPS; LDP1; LMN1; LMNC; MADA; PRO1; CDCD1; CMD1A; FPLD2; LMNL1; CMT2B1; LGMD1B |
| WB Predicted band size | 74 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human LMNA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于LMNA抗体的代表性文献摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to lamin A/C in patients with autoimmune hepatitis*
**作者**:Wesierska-Gadek et al.
**摘要**:研究发现部分自身免疫性肝炎(AIH)患者血清中存在针对核纤层蛋白A/C(LMNA)的自身抗体,提示这些抗体可能与肝脏特异性自身免疫反应的病理机制相关,或作为疾病活动的潜在生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Anti-lamin A/C antibodies in systemic sclerosis: Clinical associations*
**作者**:Mouthon et al.
**摘要**:探讨系统性硬化症(SSc)患者中抗LMNA抗体的存在及其与疾病亚型的关系,发现抗体阳性患者更易出现心脏受累和纤维化症状,提示其可能参与器官特异性损伤。
3. **文献名称**:*Lamin A/C autoantibodies in dilated cardiomyopathy: Diagnostic implications*
**作者**:van Berlo et al.
**摘要**:研究扩张型心肌病(DCM)患者中抗LMNA抗体的检出率,发现其与遗传性LMNA突变无关,但可能反映心肌细胞损伤后释放的自身抗原触发的继发性免疫反应。
---
如需更多文献或具体研究细节,可进一步补充关键词或限定研究领域。
The LMNA antibody targets proteins encoded by the LMNA gene, primarily lamin A and lamin C, which are critical components of the nuclear lamina. These intermediate filament proteins provide structural support to the nucleus, regulate chromatin organization, and influence gene expression, cell cycle progression, and DNA repair. LMNA mutations are linked to a spectrum of disorders termed laminopathies, including Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS), Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD), and dilated cardiomyopathy.
LMNA antibodies are essential tools in research and diagnostics. In research, they enable the detection and localization of lamin A/C isoforms via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and immunofluorescence, helping to study nuclear morphology and disease mechanisms. Clinically, these antibodies aid in diagnosing laminopathies by identifying abnormal protein expression or mislocalization in patient samples. They also contribute to understanding the pathological effects of LMNA mutations, such as nuclear envelope instability or altered interactions with chromatin-associated proteins.
Recent studies explore LMNA antibodies in therapeutic contexts, including monitoring antisense oligonucleotide therapies in progeria. However, challenges remain, such as ensuring antibody specificity given lamin isoforms' structural similarities and cross-reactivity risks. Advances in antibody validation and epitope mapping continue to enhance their reliability in both basic and translational studies of LMNA-related diseases.
×