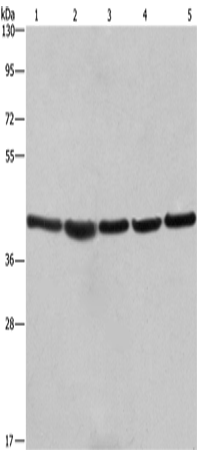
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
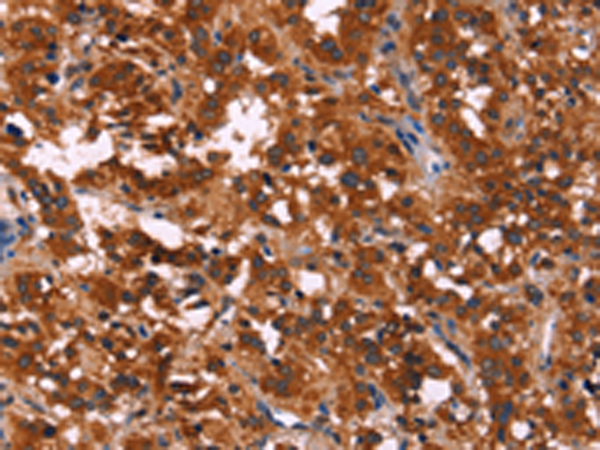
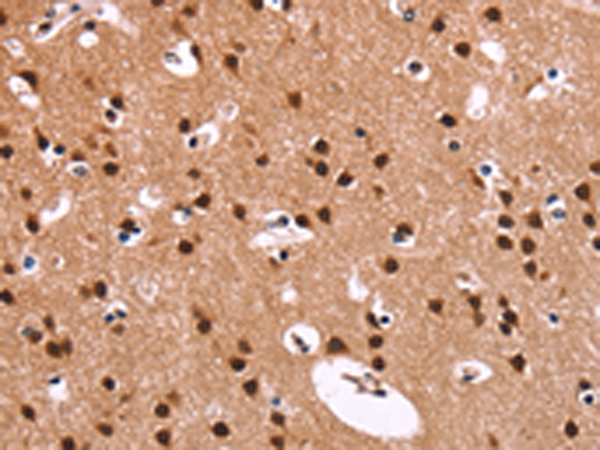
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SA; LBP; LRP; p40; 67LR; lamR; 37LRP; LAMBR; LAMR1; LRP/LR; LBP/p40; NEM/1CHD4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 33 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human RPSA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于RPSA抗体的参考文献及其摘要内容概述:
---
1. **文献名称**: *"Monoclonal antibody targeting ribosomal protein SA enhances chemosensitivity in breast cancer"*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 研究开发了一种靶向RPSA的单克隆抗体,发现其可通过抑制RPSA介导的PI3K/AKT信号通路增强乳腺癌细胞对化疗药物的敏感性,为RPSA抗体的治疗潜力提供实验依据。
---
2. **文献名称**: *"Ribosomal protein SA as a novel biomarker for early-stage colorectal cancer detection"*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 通过免疫组化分析发现,RPSA抗体在结直肠癌早期组织中的高表达特性,提示RPSA可能作为新型诊断标志物,其抗体可用于临床样本的检测和预后评估。
---
3. **文献名称**: *"Functional characterization of anti-RPSA antibodies in suppressing tumor cell invasion"*
**作者**: Lee S, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用抗RPSA抗体阻断肿瘤细胞与细胞外基质的相互作用,证实RPSA在癌细胞侵袭转移中的关键作用,并证明抗体可显著抑制体内外肿瘤侵袭能力。
---
如需具体文献来源或补充年份/期刊信息,可进一步说明。
Ribosomal Protein SA (RPSA), also known as LamR1 (Laminin Receptor 1) or 37/67 kDa laminin receptor, is a multifunctional protein encoded by the RPSA gene. Initially identified as a ribosomal component involved in protein biosynthesis, RPSA was later discovered to function as a cell-surface receptor for laminin, a key extracellular matrix protein. This dual role links RPSA to diverse cellular processes, including ribosome assembly, cell adhesion, migration, and signaling. Structurally, RPSA comprises an N-terminal ribosomal-binding domain and a C-terminal laminin-binding domain, enabling its participation in both intracellular translational machinery and extracellular matrix interactions.
RPSA antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in physiological and pathological contexts. In cancer research, RPSA overexpression is associated with tumor progression and metastasis, as laminin-mediated interactions promote invasive behavior. Antibodies targeting RPSA help detect its expression in tumor tissues or evaluate its role in cancer cell migration assays. In neurodegenerative diseases, RPSA is implicated in prion protein and amyloid-β trafficking, making these antibodies valuable for investigating Alzheimer’s or prion disease mechanisms. Additionally, RPSA serves as a receptor for pathogens like dengue virus and *Staphylococcus aureus*, highlighting its relevance in infectious disease studies. Commercial RPSA antibodies include monoclonal and polyclonal variants, often validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and flow cytometry. Ongoing research continues to explore RPSA’s therapeutic potential as a biomarker or drug target.
×