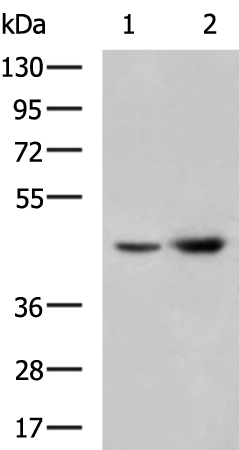
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
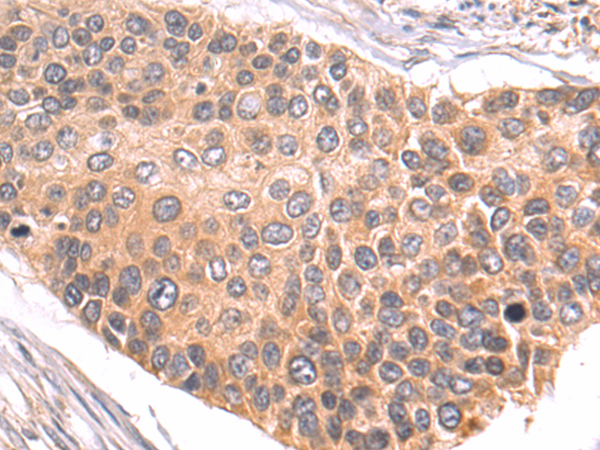
| IHC | 1/100-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | MIC-A; PERB11.1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 43 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human MICA |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于MICA抗体的代表性文献(信息已简化概括):
---
1. **文献名称**: *MICA Antibodies in Immunized Patients Wait-Listed for Kidney Transplant*
**作者**: Klooster G. et al.
**摘要**: 研究揭示了肾移植等待者体内预存的MICA抗体与移植后急性排斥反应的相关性,提示检测MICA抗体可能优化器官分配策略。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Anti-MICA Antibodies Are Associated with Reduced Kidney Allograft Survival*
**作者**: El-Awar N. et al.
**摘要**: 通过大样本分析,证实MICA抗体(尤其是IgG亚型)是独立于HLA抗体的移植肾失功风险因素,强调移植前需联合检测两类抗体。
---
3. **文献名称**: *MICA SNPs and Anti-MICA Antibodies as Biomarkers of Chronic GVHD*
**作者**: Suárez-Alvarez B. et al.
**摘要**: 发现MICA基因多态性引发的同种异体抗体与异基因造血干细胞移植后慢性移植物抗宿主病(cGVHD)发生率升高相关,为免疫监测提供新靶点。
---
**领域意义**:这些研究共同指向MICA抗体在移植免疫中的病理作用,推动临床检测标准化及靶向治疗策略的发展。如需具体年份或期刊信息可进一步补充。
MICA (MHC class I chain-related molecule A) is a stress-inducible glycoprotein belonging to the non-classical MHC class I family. It is encoded within the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) region and expressed on epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells, particularly under cellular stress, viral infection, or malignant transformation. MICA interacts with the activating receptor NKG2D on natural killer (NK) cells, γδ T cells, and CD8+ αβ T cells, triggering cytotoxic responses against stressed or infected cells.
MICA antibodies arise in contexts where immune recognition of MICA is disrupted. In organ transplantation, MICA mismatches between donor and recipient can induce alloantibodies, contributing to graft rejection and vasculopathy. These antibodies may activate endothelial cells via complement-dependent pathways or antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity. In autoimmune diseases, abnormal MICA expression on tissues may promote autoantibody production. In cancer, tumor cells often shed soluble MICA (sMICA) to evade NKG2D-mediated immune surveillance. Anti-MICA antibodies might neutralize sMICA, restoring antitumor immunity, though their role remains controversial.
MICA's extensive polymorphism (>100 alleles) complicates antibody detection and clinical interpretation. Research focuses on understanding MICA antibody pathogenicity, diagnostic utility in transplant monitoring, and therapeutic potential in cancer immunotherapy. Challenges include standardizing detection assays and clarifying mechanisms linking MICA antibodies to disease progression or protection.
×