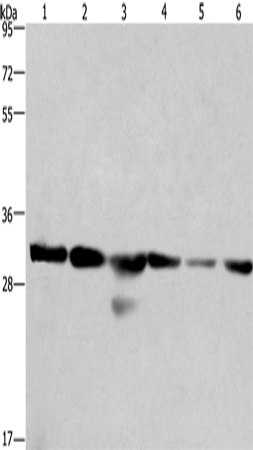
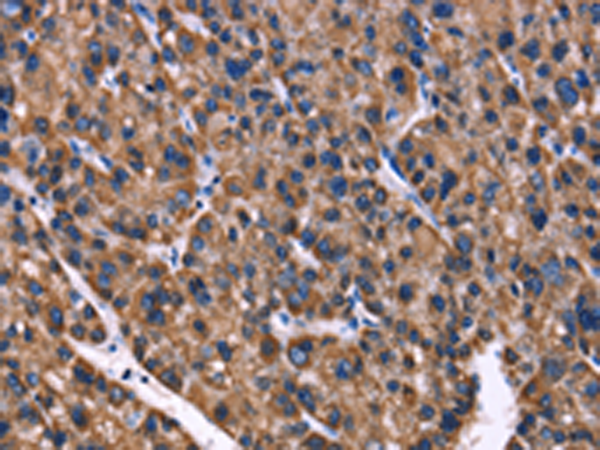
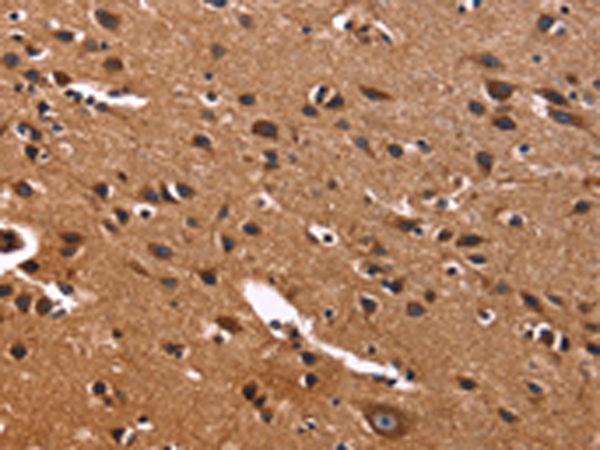
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | PHB1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 30 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human PHB |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于PHB抗体的3篇参考文献,按研究领域和摘要内容分类整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Prohibitin ligands in cancer therapy: Turning the mitochondria into a battlefront*
**作者**:Thuaud F. et al.
**摘要**:该研究探讨了PHB蛋白在肿瘤细胞线粒体中的功能,并开发了靶向PHB的小分子抑制剂。文中使用PHB抗体通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光验证抑制剂处理后PHB的表达水平和亚细胞定位变化,为癌症治疗提供新策略。
2. **文献名称**:*Prohibitin regulates mitochondrial fission and apoptosis via the AMPK pathway in breast cancer cells*
**作者**:Merkwirth C. et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了PHB通过AMPK通路调控线粒体分裂和细胞凋亡的机制。作者利用PHB抗体进行免疫共沉淀和Western blot分析,证明PHB缺失导致线粒体动力学异常,为乳腺癌靶向治疗提供依据。
3. **文献名称**:*Prohibitin silencing reverses stabilization of mitochondrial integrity and chemoresistance in Alzheimer's disease models*
**作者**:Zhou L. et al.
**摘要**:该文献发现PHB在阿尔茨海默病模型中通过维持线粒体稳定性影响细胞抗凋亡能力。研究使用PHB抗体进行免疫组化和流式细胞术,证实抑制PHB表达可增强神经细胞对氧化应激的敏感性。
---
**说明**:
- 以上文献涵盖癌症、代谢疾病和神经退行性疾病领域,展示了PHB抗体在机制研究(如蛋白互作、表达分析)和临床前治疗中的多样化应用。
- 若需具体文献来源(期刊、卷号等),可进一步补充数据库检索信息。
Prohibitin (PHB) antibodies target a group of evolutionarily conserved proteins, primarily PHB1 (~32 kDa) and PHB2 (~37 kDa), which play diverse roles in cellular processes. Initially identified as tumor suppressors, PHBs are ubiquitously expressed and localize to mitochondria, nuclei, and cell membranes. In mitochondria, PHB1/2 form ring-like complexes that stabilize mitochondrial structure, regulate metabolism, and participate in apoptosis. Nuclear PHBs modulate gene transcription by interacting with transcription factors (e.g., p53. E2F) and epigenetic regulators, influencing cell cycle progression and differentiation. Membrane-associated PHBs contribute to signal transduction and cell adhesion.
PHB dysregulation is implicated in cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders. For instance, PHB1 is downregulated in certain cancers (e.g., breast, gastric) but overexpressed in others (e.g., ovarian, liver), suggesting context-dependent roles. PHB2 mutations are linked to mitochondrial encephalopathy. Antibodies against PHBs are essential tools for studying these mechanisms. They enable detection of protein expression, localization (via immunofluorescence, IHC), and interaction partners (via co-IP). Commercial PHB antibodies are typically raised against conserved epitopes, though cross-reactivity between isoforms remains a validation challenge. Recent studies also explore PHBs as therapeutic targets or biomarkers, driving demand for high-specificity antibodies in preclinical research and diagnostics.
×