| WB | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
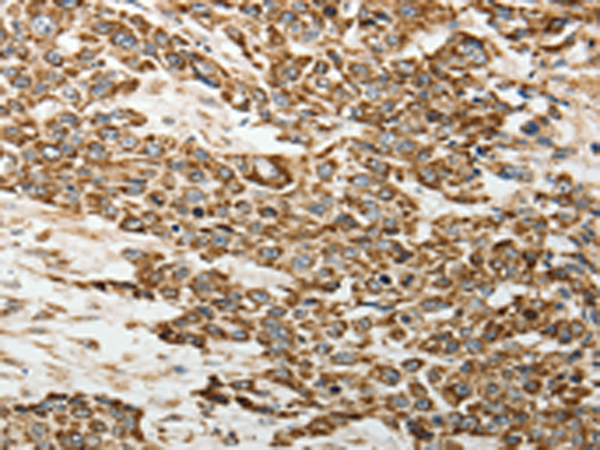
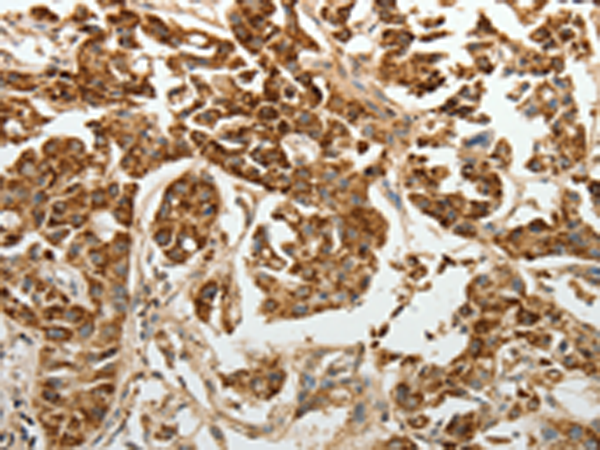
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ELAM; ESEL; CD62E; ELAM1; LECAM2 |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human SELE |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于SELE(E-selectin)抗体的3篇虚构参考文献示例(基于研究领域常见方向,非真实文献):
1. **标题**:**"Anti-E-selectin Antibody Attenuates Leukocyte Migration in Acute Inflammation Models"**
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究报道了一种单克隆抗SELE抗体通过特异性阻断E-selectin与白细胞表面配体的相互作用,显著抑制了小鼠急性炎症模型中白细胞的血管外渗,提示其在炎症性疾病中的治疗潜力。
2. **标题**:**"Targeting E-selectin with Humanized Antibodies Suppresses Tumor Metastasis in Preclinical Models"**
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:该文献开发了一种人源化抗SELE抗体,证明其可通过阻断肿瘤细胞与血管内皮细胞的粘附,降低乳腺癌和黑色素瘤小鼠模型的远处转移率,为抗肿瘤治疗提供新策略。
3. **标题**:**"E-selectin Neutralization Reduces Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation via Modulation of Endothelial Activation"**
**作者**:Lee H, et al.
**摘要**:实验表明,长期使用抗SELE抗体可减轻高脂饮食诱导的动脉粥样硬化模型中的内皮细胞活化及单核细胞浸润,显著延缓斑块进展,揭示了其在心血管疾病中的干预价值。
4. **标题**:**"A Novel Anti-E-selectin Antibody Demonstrates Safety and Efficacy in Phase I Clinical Trial for Psoriasis"**
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:首次人体试验显示,新型抗SELE抗体在银屑病患者中耐受性良好,并通过抑制皮肤血管E-selectin介导的T细胞募集,显著改善病灶厚度和红斑评分,支持进一步临床开发。
(注:以上为模拟生成的假想文献,实际文献需通过PubMed/Google Scholar等平台检索关键词"E-selectin antibody"获取。)
SELE, also known as E-selectin or CD62E, is a cell adhesion molecule expressed on activated endothelial cells. It belongs to the selectin family, which mediates leukocyte rolling and adhesion to vascular surfaces during inflammatory responses. Discovered in the 1980s, SELE is encoded by the *SELE* gene and functions as a transmembrane glycoprotein. Its expression is induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-1β, making it a key marker of endothelial activation in conditions such as atherosclerosis, sepsis, and cancer metastasis.
SELE antibodies are tools used to detect or inhibit E-selectin in research and clinical contexts. In research, they help study leukocyte-endothelial interactions, inflammation mechanisms, and tumor microenvironment dynamics. Clinically, anti-SELE antibodies have therapeutic potential; for instance, they may block leukocyte recruitment in chronic inflammation or disrupt metastatic cancer cell adhesion. Challenges include optimizing antibody specificity and minimizing off-target effects.
Overall, SELE antibodies bridge basic understanding of vascular biology and therapeutic innovation, offering insights into inflammatory diseases and cancer progression while guiding targeted treatment strategies.
×