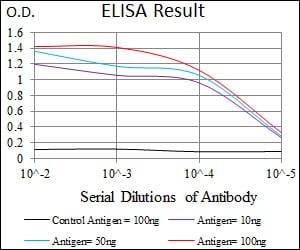
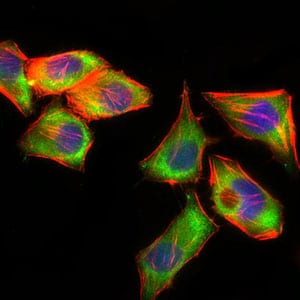
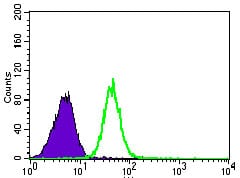
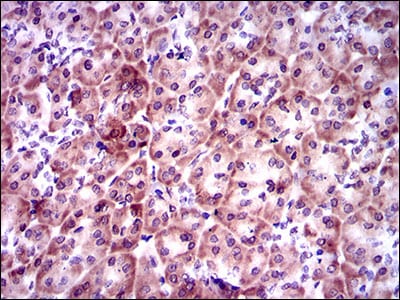
| WB | 1/1000-1/5000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/2000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | GLBA; SAP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 5660 |
| clone | 4D5F4 |
| WB Predicted band size | 58.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | Purified recombinant fragment of human PSAP (AA: 325-524 ) expressed in E. Coli. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide |
+ +
以下是关于DIABLO(SMAC)抗体的3篇经典文献,涵盖其功能研究与抗体应用:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins*
**作者**:Verhagen, A.M., et al.
**摘要**:该研究首次鉴定了DIABLO蛋白,通过生成特异性多克隆抗体,证实其在细胞凋亡过程中从线粒体释放,并与凋亡抑制蛋白(IAP)结合,解除IAP对caspase的抑制作用,从而促进细胞凋亡。
2. **文献名称**:*Smac, a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c–dependent caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition*
**作者**:Du, C., et al.
**摘要**:本研究独立发现了SMAC(即DIABLO),利用抗体通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,证明其通过拮抗IAP(如XIAP)促进caspase-9激活,并揭示了其在凋亡信号通路中的关键作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Targeting of DIABLO/SMAC for therapeutic intervention in cancer*
**作者**:Yang, Q.H., et al.
**摘要**:通过抗DIABLO抗体分析其在肿瘤组织中的表达,研究发现DIABLO在多种癌症中表达异常,并探讨了通过调控DIABLO-IAP相互作用增强化疗敏感性的潜在治疗策略。
---
以上文献均涉及DIABLO抗体的应用,包括功能验证(如Western blot、免疫荧光)及临床相关性研究,为凋亡机制及癌症治疗提供了重要依据。如需更近期研究或特定抗体开发文献,建议进一步限定时间范围或应用场景。
The DIABLO (Direct IAP-Binding Protein with Low pI) protein, also known as Smac (Second mitochondria-derived activator of caspases), is a mitochondrial pro-apoptotic factor critical for regulating programmed cell death. It is released into the cytosol during apoptosis, where it neutralizes inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) by binding to them, thereby relieving their suppression of caspase activity. This interaction promotes caspase activation and execution of apoptosis.
Antibodies targeting DIABLO/Smac are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in cellular pathways. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to assess DIABLO levels in cancer research, as dysregulation of DIABLO is linked to tumor progression and chemoresistance. Reduced DIABLO expression in some cancers correlates with evasion of apoptosis, making it a potential biomarker or therapeutic target.
Additionally, DIABLO antibodies aid in exploring its role in neurodegenerative diseases and ischemic injuries, where impaired apoptosis regulation contributes to pathology. The development of SMAC mimetics—small molecules mimicking DIABLO’s IAP-binding function—highlights its therapeutic relevance. These mimetics, combined with antibody-based studies, advance understanding of apoptosis mechanisms and strategies to restore cell death sensitivity in treatment-resistant diseases. Research on DIABLO continues to uncover its broader roles in cellular stress responses and immune regulation.
×