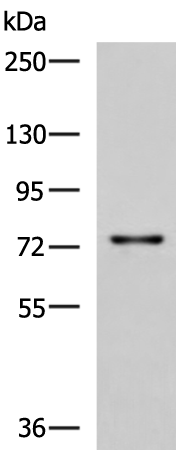
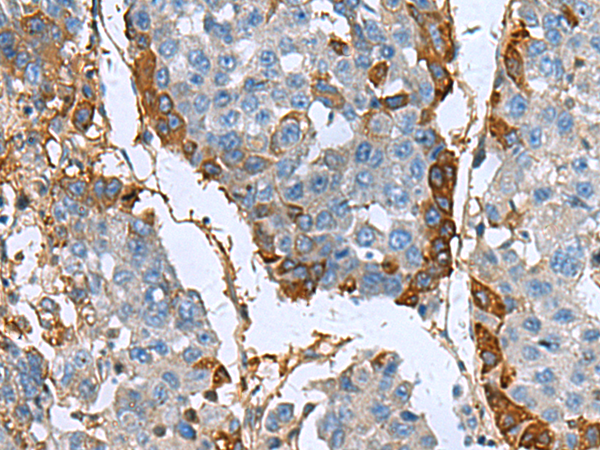
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/50-1/200 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CSD; CDB1; CDG2; CSD1; CSD2; CSD3; EBMD; LCD1; BIGH3; CDGG1 |
| WB Predicted band size | 75 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TGFBI |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TGFBI抗体的代表性文献摘要(注:部分文献可能侧重TGFBI蛋白功能,抗体应用需结合具体研究内容):
---
1. **"TGFBI (βig-H3) is a potential target for diagnosis and therapy of corneal dystrophies"**
*作者:Kim JE, Kim EH, Han EH, Park RW, Park IH, Jun SH*
摘要:研究探讨了TGFBI蛋白在角膜营养不良患者中的突变形式,开发了特异性抗体用于检测角膜组织中异常TGFBI沉积,提出抗体在疾病早期诊断和靶向治疗中的潜力。
2. **"Antibody-based detection of TGFBI in the tumor microenvironment predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer"**
*作者:Ma C, Zhang Y, Chen X, Liu Q*
摘要:通过抗TGFBI抗体免疫组化分析发现,结直肠癌组织中TGFBI高表达与肿瘤侵袭性和患者生存率下降显著相关,提示其可作为预后标志物。
3. **"Therapeutic targeting of TGFBI in fibrosis: insights from monoclonal antibody intervention in murine models"**
*作者:Yuan Y, Li Z, Wang D, Liu H*
摘要:研究利用抗TGFBI单克隆抗体在小鼠肺纤维化模型中抑制TGF-β信号通路激活,证明抗体干预可减少胶原沉积并改善器官功能。
---
**说明**:TGFBI(Transforming Growth Factor Beta Induced)抗体研究多聚焦于其在遗传性角膜疾病、肿瘤微环境及纤维化疾病中的作用。实际文献检索建议通过PubMed等平台以“TGFBI antibody”或“anti-TGFBI”为关键词筛选近5年研究。
TGFBI antibodies target the protein product of the *TGFBI* (Transforming Growth Factor Beta-Induced) gene, also known as *BIGH3* or *keratoepithelin*. This gene encodes a secreted extracellular matrix (ECM) protein involved in cell adhesion, migration, and differentiation. TGFBI interacts with integrins and collagen, modulating cell-ECM communication. Mutations in *TGFBI* are linked to inherited corneal dystrophies, such as lattice corneal dystrophy and granular corneal dystrophy, where abnormal protein aggregates form in the cornea, leading to vision impairment.
In autoimmune or inflammatory conditions, TGFBI can act as an autoantigen. Antibodies against TGFBI are rarely reported but may emerge in pathologies involving ECM remodeling, such as fibrosis or certain cancers. In cancer, TGFBI has dual roles: it can suppress tumor growth by promoting apoptosis or enhance metastasis by facilitating cell invasion, depending on the tumor microenvironment. TGFBI antibodies are thus explored as potential biomarkers or therapeutic tools in oncology.
Research tools like monoclonal TGFBI antibodies are widely used to study protein localization, expression patterns, and pathological mechanisms in corneal diseases or cancer models. Their diagnostic utility includes detecting TGFBI deposits in corneal biopsies or monitoring TGFBI levels in bodily fluids as a disease progression indicator. Further studies aim to clarify TGFBI's context-dependent functions and therapeutic targeting potential.
×