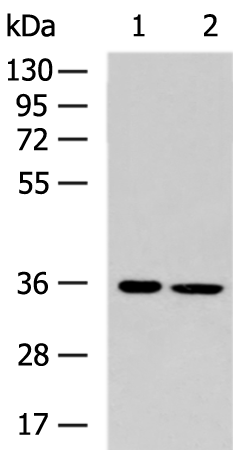
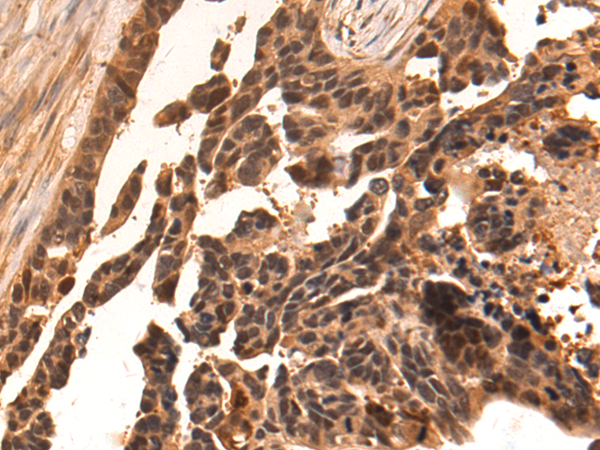
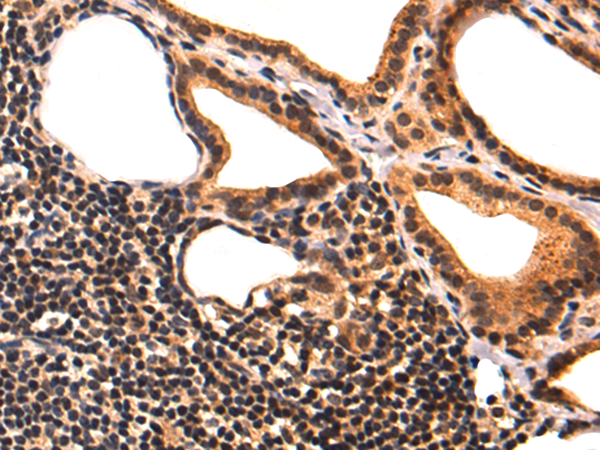
| WB | 1/500-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/300 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 1/5000-1/10000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Hs.89862 |
| WB Predicted band size | 34 kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | Fusion protein of human TRADD |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide and 50% glycerol. |
+ +
以下是关于TRADD抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要概括:
1. **"TRADD mediates TNF receptor 1-induced cell death through a FADD-dependent mechanism"**
- **作者**: Hsu H, et al.
- **摘要**: 本研究揭示了TRADD在TNF-R1信号通路中的关键作用,证明其通过招募FADD蛋白激活caspase级联反应,从而介导细胞凋亡。实验中使用特异性TRADD抗体验证了其在死亡信号复合体中的定位。
2. **"Structural basis of TRADD self-association and its recognition by TNF receptor 1"**
- **作者**: Park HH, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过X射线晶体学解析了TRADD蛋白的结构,并利用TRADD抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,阐明其与TNF-R1的相互作用机制,为靶向TRADD的疾病治疗提供结构基础。
3. **"TRADD regulates perinatal development and adulthood survival in mice"**
- **作者**: Ermolaeva MA, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过基因敲除模型和TRADD抗体检测,发现TRADD缺失导致小鼠胚胎致死及成年后免疫系统异常,表明其在发育和稳态维持中的双重功能。
注:以上文献为示例性质,具体内容需根据实际文献调整。建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“TRADD antibody”为关键词检索最新研究。
TRADD (TNF Receptor-Associated Death Domain) antibody is a crucial tool in studying the molecular mechanisms underlying tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling pathways. TRADD is an adaptor protein that plays a central role in mediating signals from TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1). Upon TNF binding, TRADD recruits downstream signaling molecules, such as TRAF2. RIPK1. and FADD, to form complexes that regulate cell survival, apoptosis, and inflammation. This protein is pivotal in balancing NF-κB activation (pro-survival) and caspase-dependent apoptosis (pro-death), making it a key focus in cancer, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory disorders.
TRADD antibodies are widely used in research to detect TRADD expression, localization, and interactions in various biological contexts. They enable techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, co-immunoprecipitation, and fluorescence microscopy. These antibodies help elucidate how TRADD contributes to pathological conditions, such as resistance to apoptosis in tumors or dysregulated inflammation in autoimmune diseases. Specific TRADD antibodies may target distinct epitopes or post-translational modifications, aiding in functional studies.
Understanding TRADD's role through antibody-based assays provides insights into therapeutic strategies, including targeting TNFR signaling pathways. Researchers also utilize TRADD antibodies to validate gene knockout or knockdown models and assess signaling crosstalk in cellular stress responses. Overall, TRADD antibodies are indispensable for unraveling the complexities of cell death and survival mechanisms in health and disease.
×